Th17 Lymphocytes in Children with Asthma: Do They Influence Control?
- PMID: 34958246
- PMCID: PMC8817680
- DOI: 10.1089/ped.2021.0067
Th17 Lymphocytes in Children with Asthma: Do They Influence Control?
Abstract
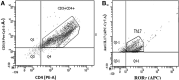
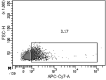
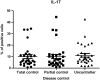
Background: Allergic asthma was considered as an inflammation mediated by specific CD4+ helper lymphocytes (Th2); however, this paradigm changed in 2005, when a third group of helper cells called Th17 cells were identified. Th17 lymphocytes are the main source of interleukin (IL)-17A-F, IL-21, and IL-22; however, their physiological role in children is unclear. This study aimed to determine the percentage of Th17 cells and IL-17A in pediatric patients diagnosed with asthma and to associate it with disease control using a validated questionnaire. Methods: This cross-sectional, prospective, comparative study included 92 asthma-diagnosed children 4-18 years of age. The Asthma Control Test was used as an assessment measure to classify patients as controlled (n = 30), partially controlled (n = 31), and uncontrolled (n = 31). Th17 cells and IL-17A were analyzed by flow cytometry. Patients receiving inhaled steroid therapy as monotherapy or associated with a long-acting bronchodilator were included. Results: The mean percentage of Th17 cells in the participants was 4.55 ± 7.34 (Controlled), 5.50 ± 8.09 (Partially Controlled), and 6.14 ± 7.11 (Uncontrolled). There was no significant difference between the 3 groups (P = 0.71). The mean percentage of IL-17A in all the participants was 9.84 ± 9.4 (Controlled), 10.10 ± 10.5 (Partially Controlled), and 11.42 ± 8.96 (Uncontrolled); no significant difference between the 3 groups (P = 0.79) was observed. Th17 lymphocyte levels were similar among the 3 groups and the same trend was observed with IL-17A. A significant correlation between Th17 or IL-17A and the degree of asthma control (Th17, P = 0.24; IL-17A, P = 0.23) was not found. Conclusions: The percentages of both Th17 lymphocytes and IL-17A found in children with asthma were not significantly different in the 3 groups, which suggests that they do not play an important role in asthma control. Our findings may contribute to the knowledge related to non-Th2 inflammation in children. Clinical-Trials.gov ID: 2015-2102-85.
Keywords: Th17 lymphocytes; asthma; children; control; interleukin 17.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Lötvall J, Akdis CA, Bacharier LB, et al. . Asthma endotypes: a new approach to classification of disease entities within the asthma syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2011; 127:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Desai M, Oppenheimer J. Elucidating asthma phenotypes and endotypes: progress towards personalized medicine. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol 2016; 116:394401. - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Initiative for Asthma: global strategy for asthma management and prevention (Updated 2020). 2020; 36:685–704.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

