Antiviral Activities of Eucalyptus Essential Oils: Their Effectiveness as Therapeutic Targets against Human Viruses
- PMID: 34959612
- PMCID: PMC8706319
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14121210
Antiviral Activities of Eucalyptus Essential Oils: Their Effectiveness as Therapeutic Targets against Human Viruses
Abstract
Given the limited therapeutic management of infectious diseases caused by viruses, such as influenza and SARS-CoV-2, the medicinal use of essential oils obtained from Eucalyptus trees has emerged as an antiviral alternative, either as a complement to the treatment of symptoms caused by infection or to exert effects on possible pharmacological targets of viruses. This review gathers and discusses the main findings on the emerging role and effectiveness of Eucalyptus essential oil as an antiviral agent. Studies have shown that Eucalyptus essential oil and its major monoterpenes have enormous potential for preventing and treating infectious diseases caused by viruses. The main molecular mechanisms involved in the antiviral activity are direct inactivation, that is, by the direct binding of monoterpenes with free viruses, particularly with viral proteins involved in the entry and penetration of the host cell, thus avoiding viral infection. Furthermore, this review addresses the coadministration of essential oil and available vaccines to increase protection against different viruses, in addition to the use of essential oil as a complementary treatment of symptoms caused by viruses, where Eucalyptus essential oil exerts anti-inflammatory, mucolytic, and spasmolytic effects in the attenuation of inflammatory responses caused by viruses, in particular respiratory diseases.
Keywords: 1,8-cineole; Eucalyptus essential oil; H1N1 influenza virus; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral therapy; herpes simplex virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

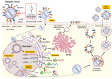
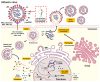
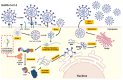
References
-
- Chandorkar N., Tambe S., Amin P., Madankar C. A systematic and comprehensive review on current understanding of the pharmacological actions, molecular mechanisms, and clinical implications of the genus Eucalyptus. Phyto. Plus. 2021;1:100089. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100089. - DOI
-
- Ballesta P., Serra N., Guerra F.P., Hasbún R., Mora F. Genomic Prediction of Growth and Stem Quality Traits in Eucalyptus globulus Labill. at Its Southernmost Distribution Limit in Chile. Forests. 2018;9:779. doi: 10.3390/f9120779. - DOI
-
- Mora F., Ballesta P., Serra N. Bayesian analysis of growth, stem straightness and branching quality in full-sib families of Eucalyptus globulus. Bragantia. 2019;78:328–336. doi: 10.1590/1678-4499.20180317. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

