FXR, a Key Regulator of Lipid Metabolism, Is Inhibited by ER Stress-Mediated Activation of JNK and p38 MAPK in Large Yellow Croakers (Larimichthys crocea) Fed High Fat Diets
- PMID: 34959897
- PMCID: PMC8706856
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124343
FXR, a Key Regulator of Lipid Metabolism, Is Inhibited by ER Stress-Mediated Activation of JNK and p38 MAPK in Large Yellow Croakers (Larimichthys crocea) Fed High Fat Diets
Abstract
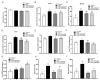
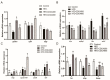
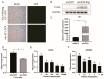
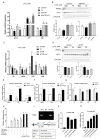
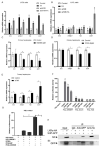
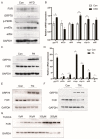
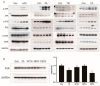
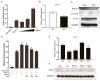
High-fat diets induced abnormal lipid accumulation in the liver of cultured fish that caused body damage and diseases. The purpose of this research was to investigate the role and mechanism of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) in regulating lipid metabolism and to determine how high-fat diets affect FXR expression in large yellow croakers. The results showed that ligand-meditated FXR-activation could prevent abnormal lipid accumulation in the liver and hepatocytes of large yellow croakers. FXR activation increased the expression of lipid catabolism-related genes while decreasing the expression of lipogenesis-related genes. Further investigation found that the promoter activity of proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) could be increased by croaker FXR. Through the influence of SHP on LXR, FXR indirectly decreased the promoter activity of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (SREBP1) in large yellow croakers. Furthermore, the findings revealed that endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-stress-induced-activation of JNK and P38 MAPK participated in the reduction of FXR induced by high-fat diets. Then, hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1α) was confirmed to be an FXR regulator in large yellow croaker, and it was reduced by high-fat diets and ER stress. In addition, co-expression of c-Jun with HNF1α inhibited the effect of HNF1α on FXR promoter, and suppression of P38 MAPK could relieve the HNF1α expression reduction caused by ER stress activation. In summary, the present study showed that FXR mediated lipid metabolism can prevent abnormal lipid accumulation through regulating PPARα and SREBP1 in large yellow croakers, while high-fat diets can suppress FXR expression by ER stress mediated-activation of JNK and P38 MAPK pathways. This research could benefit the study of FXR functions in vertebrate evolution and the development of therapy or preventative methods for nutrition-related disorders.
Keywords: ER stress; FXR; MAPK; high-fat diets; lipid metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Suppresses Linoleic Acid-Induced Inflammation in the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea).J Nutr. 2020 Sep 1;150(9):2469-2477. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa185. J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32614453
-
High level of dietary olive oil decreased growth, increased liver lipid deposition and induced inflammation by activating the p38 MAPK and JNK pathways in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Nov;94:157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.08.062. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31465874
-
Activation of farnesoid X receptor suppresses ER stress and inflammation via the YY1/NCK1/PERK pathway in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 24;9:1024631. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1024631. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36505250 Free PMC article.
-
A new perspective on NAFLD: Focusing on the crosstalk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and farnesoid X receptor (FXR).Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Oct;154:113577. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113577. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35988420 Review.
-
Regulation of Liver Energy Balance by the Nuclear Receptors Farnesoid X Receptor and Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor α.Dig Dis. 2017;35(3):203-209. doi: 10.1159/000450912. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Dig Dis. 2017. PMID: 28249296 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell death in liver injury.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 19;13(12):1051. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05444-x. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36535923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin Regulates Lipid Metabolism and Fat Accumulation by Regulating Inflammatory Responses and Glycometabolism Pathways: A Review.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 9;16(8):1102. doi: 10.3390/nu16081102. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Farnesoid X Receptor as a Master Regulator of Hepatotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 12;23(22):13967. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213967. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environment, Endocrine Disruptors, and Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction (MASLD).Metabolites. 2024 Jan 22;14(1):71. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010071. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38276306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorder Caused by NaAsO2 through Regulating the ERK/PPAR Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 14;2022:6405911. doi: 10.1155/2022/6405911. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9847073. doi: 10.1155/2024/9847073. PMID: 35320977 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31525024/the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China
- 31830103/the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018YFD0900402/the Scientific and Technological Innovation of Blue Granary
- CARS-47-11/the Agriculture Research System of China
- 2018-29/the Ten-thousand Talents Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

