Effect and Tolerability of a Nutritional Supplement Based on a Synergistic Combination of β-Glucans and Selenium- and Zinc-Enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ABB C1®) in Volunteers Receiving the Influenza or the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
- PMID: 34959898
- PMCID: PMC8708701
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124347
Effect and Tolerability of a Nutritional Supplement Based on a Synergistic Combination of β-Glucans and Selenium- and Zinc-Enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ABB C1®) in Volunteers Receiving the Influenza or the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
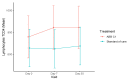
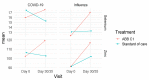
A single-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 72 volunteers who received a synergistic combination of yeast-based ingredients with a unique β-1,3/1,6-glucan complex and a consortium of heat-treated probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae rich in selenium and zinc (ABB C1®) or placebo on the next day after getting vaccinated against influenza (Chiromas®) (n = 34) or the COVID-19 (Comirnaty®) (n = 38). The duration of treatment was 30 and 35 days for the influenza and COVID-19 vaccine groups, respectively. Mean levels of CD4+T cells increased from 910.7 at baseline to 1000.2 cells/µL after the second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine in the ABB C1® group, whereas there was a decrease from 1055.1 to 929.8 cells/µL in the placebo group. Changes of CD3+T and CD8+T lymphocytes showed a similar trend. In the COVID-19 cohort, the increases in both IgG and IgM were higher in the ABB C1® supplement than in the placebo group. Serum levels of selenium and zinc showed a higher increase in subjects treated with the active product than in those receiving placebo. No serious adverse events related to ABB C1® or tolerance issues were reported. The study findings validate the capacity of the ABB C1® product to stimulate trained immunity.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; influenza vaccine; nutritional supplementation; selenium; trained immunity; zinc; β-1,3/1,6-glucan complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Amato M., Werba J.P., Frigerio B., Coggi D., Sansaro D., Ravani A., Ferrante P., Veglia F., Tremoli E., Baldassarre D. Relationship between influenza vaccination coverage rate and COVID-19 outbreak: An Italian ecological study. Vaccines. 2020;8:535. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8030535. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

