Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Glycemic Control in Prediabetes: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34960022
- PMCID: PMC8707376
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124464
Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Glycemic Control in Prediabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
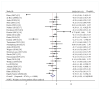
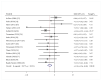
Clinical research results of vitamin D supplementation in the improvement of prediabetes remain controversial. Accordingly, a literature search was conducted of PubMed, Embase (Ovid), and Web of Science prior to 9 November 2021. Randomized controlled studies reported that the following indicators were included: body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose (FBG), 2 h oral glucose tolerance test plasma glucose (2h-PG), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), insulin resistance by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA-IR), homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-B), and fasting insulin (FINS). Twenty-nine articles (N = 3792) were included in the present meta-analysis. Intriguingly, vitamin D supplementation resulted in a vast improvement in FBG (standardized mean difference (SMD) = -0.38; 95%CI: -0.59, -0.16), HbA1c (SMD = -0.14; 95%CI: -0.22, -0.06) and FINS (SMD = 0.18; 95%CI: -0.26, -0.09), but not in other outcomes. However, preferred changes were observed in subgroups, as follows: Asia (SMD2h-PG = -0.25, 95%CI: -0.45, -0.04), study duration ≥1 year (SMDHOMA-IR = -0.44, 95%CI: -0.81, -0.06) (SMDHOMA-B = 0.34, 95%CI: 0.01, 0.66), baseline 25(OH)D < 50 nmol/L (SMD2h-PG = -0.23, 95%CI: -0.39, -0.06), and baseline 25(OH)D ≥ 50 nmol/L (SMDHOMA-IR = -0.50, 95%CI: -0.96, -0.03). In conclusion, oral supplementation of vitamin D has shown better effects in improving FBG, HbA1c, and FINS compared with controls among prediabetics; long-term vitamin D supplementation could have additional effects in participants with vitamin D deficiency for 2h-PG, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-B.
Keywords: glycemic control; meta-analysis; prediabetes; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures



References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81872626/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82003454/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CNS-BMSG2020A63/Chinese Nutrition Society-Bright Moon Seaweed Group Nutrition and Health Research Fund
- CNS-ZD2019066/Chinese Nutrition Society-Zhendong National Physical Fitness and Health Research Fund
- 212102310219/Key R&D and Promotion Projects in Henan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

