Dose-Response of Paraxanthine on Cognitive Function: A Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Trial
- PMID: 34960030
- PMCID: PMC8708375
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124478
Dose-Response of Paraxanthine on Cognitive Function: A Double Blind, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Trial
Abstract
Paraxanthine (PXN) is a metabolite of caffeine that has recently been reported to enhance cognition at a dose of 200 mg.
Objective: To determine the acute and short-term (7-day) effects of varying doses of PXN on cognitive function and side effects.
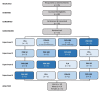
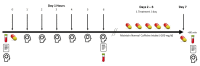
Methods: In a double blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, and counterbalanced manner, 12 healthy male and female volunteers (22.7 ± 4 years, 165 ± 7 cm, 66.5 ± 11 kg, 24.4 ± 3 kg/m2) ingested 200 mg of a placebo (PLA), 50 mg of PXN (ENFINITY™, Ingenious Ingredients, L.P.) + 150 mg PLA, 100 mg PXN + 100 mg PLA, or 200 mg of PXN. With each treatment experiment, participants completed side effect questionnaires and donated a fasting blood sample. Participants then performed a series of tests assessing cognition, executive function, memory, and reaction time. Participants then ingested one capsule of PLA or PXN treatments. Participants then completed side effects and cognitive function tests after 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 h of treatment ingestion. Participants continued ingesting one dose of the assigned treatment daily for 6-days and returned to the lab on day 7 to donate a fasting blood sample, assess side effects, and perform cognitive function tests. Participants repeated the experiment while ingesting remaining treatments in a counterbalanced manner after at least a 7-day washout period until all treatments were assessed.
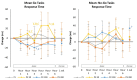
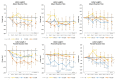
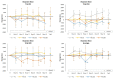
Results: The Sternberg Task Test (STT) 4-Letter Length Present Reaction Time tended to differ among groups (p = 0.06). Assessment of mean changes from baseline with 95% CI's revealed several significant differences among treatments in Berg-Wisconsin Card Sorting Correct Responses, Preservative Errors (PEBL), and Preservative Errors (PAR Rules). There was also evidence of significant differences among treatments in the Go/No-Go Task tests in Mean Accuracy as well as several time points of increasing complexity among STT variables. Finally, there was evidence from Psychomotor Vigilance Task Test assessment that response time improved over the series of 20 trials assessed as well as during the 6-h experiment in the PXN treatment. Acute and short-term benefits compared to PLA were seen with each dose studied but more consistent effects appeared to be at 100 mg and 200 mg doses. No significant differences were observed among treatments in clinical chemistry panels or the frequency or severity of reported side effects. Results provide evidence that acute ingestion of 100 mg and 200 mg of PXN may affect some measures of cognition, memory, reasoning, and response time as well as help sustain attention. Additionally, that acute and daily ingestion of PXN for 7 days is not associated with any clinically significant side effects.
Conclusions: PXN may serve as an effective nootropic agent at doses as low as 50 mg.
Keywords: caffeine alternative; mental performance; nootropics; paraxanthine.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J., M.P. and S.D.W. are researchers and principals for the sponsor of the study, and inventors of numerous patent application for the use of paraxanthine; however, they have not been involved in the data collection or analysis. R.B.K. has conducted industry sponsored research on dietary supplements through grants awarded to the universities in which he has been affiliated, received honorarium for presenting research related to dietary supplements at industry sponsored scientific conferences, has served as an expert witness on cases related to dietary supplements, and currently serves as Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board for AlzChem. He has also presented research related to nootropics at conference sessions sponsored by Nutrition 21. Other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

