Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice
- PMID: 34960054
- PMCID: PMC8706341
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124501
Dracocephalum moldavica Ethanol Extract Suppresses LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses through Inhibition of the JNK/ERK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and IL-6 Production in RAW 264.7 Macrophages and in Endotoxic-Treated Mice
Abstract
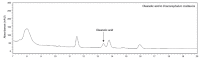
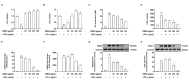
The excessive synthesis of interleukin-6 (IL-6) is related to cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients. Moreover, blocking IL-6 has been suggested as a treatment strategy for inflammatory diseases such as sepsis. Sepsis is a severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome with high mortality. In the present study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory and anti-septic effects and the underlying mechanisms of Dracocephalum moldavica ethanol extract (DMEE) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory stimulation in RAW 264.7 macrophages along with septic mouse models. We found that DMEE suppressed the release of inflammatory mediators NO and PGE2 and inhibited both the mRNA and protein expression levels of iNOS and COX-2, respectively. In addition, DMEE reduced the release of proinflammatory cytokines, mainly IL-6 and IL-1β, in RAW 264.7 cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK and p65. Furthermore, treatment with DMEE increased the survival rate and decreased the level of IL-6 in plasma in LPS-induced septic shock mice. Our findings suggest that DMEE elicits an anti-inflammatory effect in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and an anti-septic effect on septic mouse model through the inhibition of the ERK/JNK/NF-κB signaling cascades and production of IL-6.
Keywords: Dracocephalum moldavica; inflammation; interleukin-6; lipopolysaccharide; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
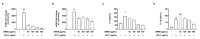
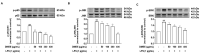

References
-
- Su Y., Xiong S., Lan H., Xu L., Wei X. Molecular mechanism underlying anti-inflammatory activities of lirioresinol B dimethyl ether through suppression of NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling in in vitro and in vivo models. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019;73:321–332. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.05.020. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 2018002270002/the Korean Ministry of Environment
- NRF-2020R1C1C1004911/the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning
- NRF-2021R1A6A1A03044242/the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) founded by the Ministry of Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

