Prenatal Iron Deficiency and Choline Supplementation Interact to Epigenetically Regulate Jarid1b and Bdnf in the Rat Hippocampus into Adulthood
- PMID: 34960080
- PMCID: PMC8706459
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13124527
Prenatal Iron Deficiency and Choline Supplementation Interact to Epigenetically Regulate Jarid1b and Bdnf in the Rat Hippocampus into Adulthood
Abstract
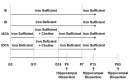
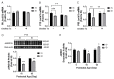
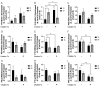
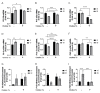
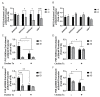
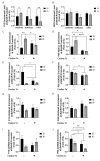
Early-life iron deficiency (ID) causes long-term neurocognitive impairments and gene dysregulation that can be partially mitigated by prenatal choline supplementation. The long-term gene dysregulation is hypothesized to underlie cognitive dysfunction. However, mechanisms by which iron and choline mediate long-term gene dysregulation remain unknown. In the present study, using a well-established rat model of fetal-neonatal ID, we demonstrated that ID downregulated hippocampal expression of the gene encoding JmjC-ARID domain-containing protein 1B (JARID1B), an iron-dependent histone H3K4 demethylase, associated with a higher histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) enrichment and a lower enrichment of acetylated histone H3K9 (H3K9ac) and phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein (pCREB). Likewise, ID reduced transcriptional capacity of the gene encoding brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a target of JARID1B, associated with repressive histone modifications such as lower H3K9ac and pCREB enrichments at the Bdnf promoters in the adult rat hippocampus. Prenatal choline supplementation did not prevent the ID-induced chromatin modifications at these loci but induced long-lasting repressive chromatin modifications in the iron-sufficient adult rats. Collectively, these findings demonstrated that the iron-dependent epigenetic mechanism mediated by JARID1B accounted for long-term Bdnf dysregulation by early-life ID. Choline supplementation utilized a separate mechanism to rescue the effect of ID on neural gene regulation. The negative epigenetic effects of choline supplementation in the iron-sufficient rat hippocampus necessitate additional investigations prior to its use as an adjunctive therapeutic agent.
Keywords: Bdnf; Jarid1b; choline; epigenetics; gene expression; histone modification; iron deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Stevens G.A., Finucane M.M., De-Regil L.M., Paciorek C.J., Flaxman S.R., Branca F., Peña-Rosas J.P., Bhutta Z.A., Ezzati M. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995-2011: A systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Glob. Health. 2013;1:e16–e25. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70001-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

