Nucleocapsid (N) Gene Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Can Affect Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic and Impact False-Negative Results
- PMID: 34960743
- PMCID: PMC8707239
- DOI: 10.3390/v13122474
Nucleocapsid (N) Gene Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Can Affect Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic and Impact False-Negative Results
Erratum in
-
Correction: Lesbon et al. Nucleocapsid (N) Gene Mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Can Affect Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic and Impact False-Negative Results. Viruses 2021, 13, 2474.Viruses. 2022 Sep 5;14(9):1967. doi: 10.3390/v14091967. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146888 Free PMC article.
Abstract
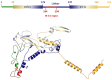
The current COVID-19 pandemic demands massive testing by Real-time RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction), which is considered the gold standard diagnostic test for the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, the virus continues to evolve with mutations that lead to phenotypic alterations as higher transmissibility, pathogenicity or vaccine evasion. Another big issue are mutations in the annealing sites of primers and probes of RT-PCR diagnostic kits leading to false-negative results. Therefore, here we identify mutations in the N (Nucleocapsid) gene that affects the use of the GeneFinder COVID-19 Plus RealAmp Kit. We sequenced SARS-CoV-2 genomes from 17 positive samples with no N gene detection but with RDRP (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) and E (Envelope) genes detection, and observed a set of three different mutations affecting the N detection: a deletion of 18 nucleotides (Del28877-28894), a substitution of GGG to AAC (28881-28883) and a frameshift mutation caused by deletion (Del28877-28878). The last one cause a deletion of six AAs (amino acids) located in the central intrinsic disorder region at protein level. We also found this mutation in 99 of the 14,346 sequenced samples by the Sao Paulo state Network for Pandemic Alert of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, demonstrating the circulation of the mutation in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Continuous monitoring and characterization of mutations affecting the annealing sites of primers and probes by genomic surveillance programs are necessary to maintain the effectiveness of the diagnosis of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; GeneFinder; N gene; RT-PCR; mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baek M., Di Maio F., Anishchenko I., Dauparas J., Ovchinnikov S., Lee G.R., Wang J., Cong Q., Kinch L.N., Schaeffer R.D., et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science. 2021;373:871–876. doi: 10.1126/science.abj8754. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 2020/10127-1/São Paulo Research Foundation
- 2020/05367-3/São Paulo Research Foundation
- 2013/08135-2/São Paulo Research Foundation
- APO21-00010098/Brazilian Ministry of Health and the Pan American Health Organization PAHO/WHO
- 401119/2020-3/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

