Genetic Dissection of Mature Root Characteristics by Genome-Wide Association Studies in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
- PMID: 34961040
- PMCID: PMC8705616
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10122569
Genetic Dissection of Mature Root Characteristics by Genome-Wide Association Studies in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
Abstract
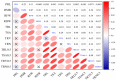
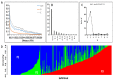
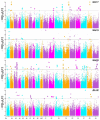
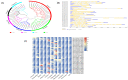
Roots are complicated quantitative characteristics that play an essential role in absorbing water and nutrients. To uncover the genetic variations for root-related traits in rapeseed, twelve mature root traits of a Brassica napus association panel were investigated in the field within three environments. All traits showed significant phenotypic variation among genotypes, with heritabilities ranging from 55.18% to 79.68%. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) using 20,131 SNPs discovered 172 marker-trait associations, including 103 significant SNPs (-log10 (p) > 4.30) that explained 5.24-20.31% of the phenotypic variance. With the linkage disequilibrium r2 > 0.2, these significant associations were binned into 40 quantitative trait loci (QTL) clusters. Among them, 14 important QTL clusters were discovered in two environments and/or with phenotypic contributions greater than 10%. By analyzing the genomic regions within 100 kb upstream and downstream of the peak SNPs within the 14 loci, 334 annotated genes were found. Among these, 32 genes were potentially associated with root development according to their expression analysis. Furthermore, the protein interaction network using the 334 annotated genes gave nine genes involved in a substantial number of interactions, including a key gene associated with root development, BnaC09g36350D. This research provides the groundwork for deciphering B. napus' genetic variations and improving its root system architecture.
Keywords: Brassica napus; GWAS; QTL; candidate genes; root traits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
- 2020BBB061/Key Research and Development Program in Hubei Province
- CAAS-ZDRW202109/Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project
- 2019CFB617/Natural Foundation of Hubei Province
- CAAS-ASTIP-2013-OCRI/Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project
- CARS-12/China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

