Microtensiometers Accurately Measure Stem Water Potential in Woody Perennials
- PMID: 34961251
- PMCID: PMC8709327
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10122780
Microtensiometers Accurately Measure Stem Water Potential in Woody Perennials
Abstract
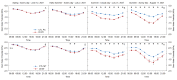
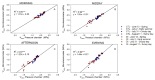
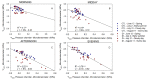
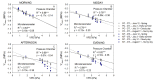
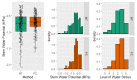
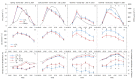
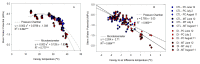
Stem water potential (Ψstem) is considered to be the standard measure of plant water status. However, it is measured with the pressure chamber (PC), an equipment that can neither provide continuous information nor be automated, limiting its use. Recent developments of microtensiometers (MT; FloraPulse sensors), which can continuously measure water tension in woody tissue of the trunk of the tree, can potentially highlight the dynamic nature of plant water relations. Thus, this study aimed to validate and assess the usefulness of the MT by comparing the Ψstem provided by MT with those same measurements from the PC. Here, two irrigation treatments (a control and a deficit treatment) were applied in a pear (Pyrus communis L.) orchard in Washington State (USA) to capture the full range of water potentials in this environment. Discrete measurements of leaf gas exchange, canopy temperature and Ψstem measured with PC and MT were made every two hours for four days from dawn to sunset. There were strong linear relationships between the Ψstem-MT and Ψstem-PC (R2 > 0.8) and with vapor pressure deficit (R2 > 0.7). However, Ψstem-MT was more variable and lower than Ψstem-PC when Ψstem-MT was below -1.5 MPa, especially during the evening. Minimum Ψstem-MT occurred later in the afternoon compared to Ψstem-PC. Ψstem showed similar sensitivity and coefficients of variation for both PC and MT acquired data. Overall, the promising results achieved indicated the potential for MT to be used to continuously assess tree water status.
Keywords: gas exchange; irrigation scheduling; pear; precision agriculture; pressure chamber; sensors; tree water status; vapor pressure deficit; water stress indicators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jones H.G. Irrigation scheduling—Comparison of soil, plant and atmosphere monitoring approaches. Acta Hortic. 2008;792:391–403. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.792.46. - DOI
-
- Sui R. Irrigation Scheduling Using Soil Moisture Sensors. J. Agric. Sci. 2017;10:1–11. doi: 10.5539/jas.v10n1p1. - DOI
-
- Pereira L.S., Paredes P., Jovanovic N. Soil Water Balance Models for Determining Crop Water and Irrigation Requirements and Irrigation Scheduling Focusing on the FAO56 Method and the Dual Kc Approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2020;241:106357. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106357. - DOI
-
- Fernández J.E. Plant-Based Methods for Irrigation Scheduling of Woody Crops. Horticulturae. 2017;3:35. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae3020035. - DOI
-
- Shackel K. A Plant-Based Approach to Deficit Irrigation in Trees and Vines. HortScience. 2011;46:173–177. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.46.2.173. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

