Development of a novel multifocal lens using a polarization directed flat lens: possible candidate for a multifocal intraocular lens
- PMID: 34961511
- PMCID: PMC8711202
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-021-02191-z
Development of a novel multifocal lens using a polarization directed flat lens: possible candidate for a multifocal intraocular lens
Abstract
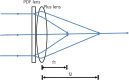
Background: A polarization-directed flat (PDF) lens acts as a converging lens with a focal length (f) > 0 and a diverging lens with f < 0, depending on the polarization state of the incidental light. To produce a multifocal lens with two focal lengths, a PDF and a converging lens having shorter focal length were combined. In this study, we tested a bifocal PDF to determine its potential as a new multifocal intraocular lens (IOL).
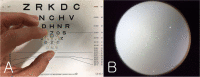
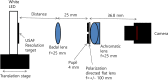
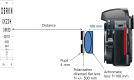
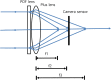
Methods: Constructed a multifocal lens with a PDF lens (f = +/- 100 mm) and a converging lens (f = + 25 mm). In an optical bench test, we measured the defocus curve to test the multifocal function. The multifocal function and optical quality of the lens in various situations were tested. An Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) chart as a near target and a building as a distant target were photographed using a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera. Both lenses (multifocal and monofocal) were tested under the same conditions.
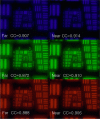
Results: For the 0 D and - 20 D focal points, the multifocal lens showed sharp images in the optical bench test. In the DSLR test using the multifocal lens, the building appeared slightly blurry compared with the results using the monofocal lens. With the multifocal lens, the ETDRS chart's images became blurry as the ETDRS chart's distance decreased, but became very clear again at a certain position.
Conclusions: We confirmed the multifocal function of the multifocal lens using a PDF lens. This lens can be used as a multifocal IOL in the future.
Keywords: Multifocal lens; Polarization-directed flat: intraocular lens.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Co-author ‘Ho Sik Hwang’ is the Editorial Board Member of BMC Ophthalmology.
The authors declare that they don’t have the other competing interests.
The author (HHS) registered a Korean patent for this multifocal lens (10-2017-0130106). The other authors have no financial interest or relationship to disclose.
Figures







Similar articles
-
A Novel Intraocular Lens Simulator that Allows Patients to Experience the World Through Multifocal Intraocular Lenses Before Surgeries.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Mar 2;11(3):14. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.3.14. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35275206 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of visual outcomes with 4 intraocular lenses: Monofocal, multifocal, and extended range of vision.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018 Feb;44(2):156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2017.11.011. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2018. PMID: 29587972
-
How does the world appear to patients with multifocal intraocular lenses?: a mobile model eye experiment.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 May 6;20(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01446-5. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32375711 Free PMC article.
-
[Multifocal intraocular lenses--an assessment of current status].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1993 Jul;203(1):19-33. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1045645. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1993. PMID: 8411889 Review. German.
-
Refraction and defocus curves in eyes with monofocal and multifocal intraocular lenses.J Optom. 2023 Jul-Sep;16(3):236-243. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2023.01.005. Epub 2023 Mar 23. J Optom. 2023. PMID: 36964069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring gender-related clinical and immunological profiles in Sjögren's disease in a Chinese cohort.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Aug 20. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07616-4. Online ahead of print. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40833704
-
Geometric-phase intraocular lenses with multifocality.Light Sci Appl. 2022 Nov 2;11(1):320. doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-01016-y. Light Sci Appl. 2022. PMID: 36323667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhan T, Zou J, Xiong J, Liu X, Chen H, Yang J, Liu S, Dong Y, Wu S-T. Practical Chromatic Aberration Correction in Virtual Reality Displays Enabled by Cost-Effective Ultra-Broadband Liquid Crystal Polymer Lenses. Advanced Optical Materials. 2020;8(2):1901360. doi: 10.1002/adom.201901360. - DOI
-
- Bjelkhagen HI, Bove VM, Xiang X, Miskiewicz MN, Escuti MJ: Distortion-free broadband holograms: A novel class of elements utilizing the wavelength-independent geometric phase. In: Practical Holography XXIX: Materials and Applications. 2015.
-
- Kim J, Li Y, Miskiewicz MN, Oh C, Kudenov MW, Escuti MJ: Fabrication of ideal geometric-phase holograms with arbitrary wavefronts. Optica 2015, 2(11).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

