Rituximab Impairs B Cell Response But Not T Cell Response to COVID-19 Vaccine in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 34962357
- PMCID: PMC9011892
- DOI: 10.1002/art.42058
Rituximab Impairs B Cell Response But Not T Cell Response to COVID-19 Vaccine in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
Objective: Antibody response to the messenger RNA (mRNA) COVID-19 vaccine has been shown to be diminished in rituximab (RTX)-treated patients. We undertook this study to compare humoral and T cell responses between healthy controls, patients with autoimmune diseases treated with RTX, and those treated with other immunosuppressants, all of whom had been vaccinated with 2 doses of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
Methods: We performed anti-spike IgG and neutralization assays just before and 28 days after the second BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccine dose. The specific T cell response was assessed in activated CD4 and CD8 T cells using intracellular flow cytometry staining of cytokines (interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-2) after stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 spike peptide pools.
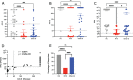
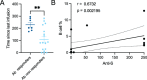
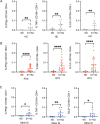
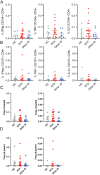
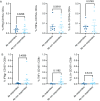
Results: A lower proportion of responders with neutralizing antibodies to the vaccine was observed in the RTX group (29%; n = 24) compared to the other immunosuppressants group (80%; n = 35) (P = 0.0001) and the healthy control group (92%; n = 26) (P < 0.0001). No patients treated with RTX in the last 6 months showed a response. Time since last infusion was the main factor influencing humoral response in RTX-treated patients. The functional CD4 and CD8 cellular responses to SARS-CoV-2 peptides for each single cytokine or polyfunctionality were not different in the RTX group compared to the other immunosuppressants group or the control group. In RTX-treated patients, the T cell response was not different between patients with and those without a humoral response.
Conclusion: RTX induced a diminished antibody response to the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, but the functional T cell response was not altered compared to healthy controls and autoimmune disease patients treated with other immunosuppressants. Further work is needed to assess the clinical protection granted by a functionally active T cell response in the absence of an anti-spike antibody response.
© 2021 American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Comment in
-
B cells: deplete, repopulate, vaccinate.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Mar;18(3):126. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00754-y. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35110747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, Peleg H, Paran D, Levartovsky D, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID‐19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: a multicentre study. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:1330–8. - PubMed
-
- Spiera R, Jinich S, Jannat‐Khah D. Rituximab, but not other antirheumatic therapies, is associated with impaired serological response to SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccination in patients with rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:1357–9. - PubMed
-
- Mrak D, Tobudic S, Koblischke M, Graninger M, Radner H, Sieghart D, et al. SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccination in rituximab‐treated patients: B cells promote humoral immune responses in the presence of T‐cell‐mediated immunity. Ann Rheum Dis 2021;80:1345–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

