EMSY inhibits homologous recombination repair and the interferon response, promoting lung cancer immune evasion
- PMID: 34963055
- PMCID: PMC8751279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.005
EMSY inhibits homologous recombination repair and the interferon response, promoting lung cancer immune evasion
Abstract
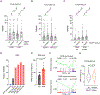
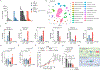
Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harboring KEAP1 mutations are often resistant to immunotherapy. Here, we show that KEAP1 targets EMSY for ubiquitin-mediated degradation to regulate homologous recombination repair (HRR) and anti-tumor immunity. Loss of KEAP1 in NSCLC induces stabilization of EMSY, producing a BRCAness phenotype, i.e., HRR defects and sensitivity to PARP inhibitors. Defective HRR contributes to a high tumor mutational burden that, in turn, is expected to prompt an innate immune response. Notably, EMSY accumulation suppresses the type I interferon response and impairs innate immune signaling, fostering cancer immune evasion. Activation of the type I interferon response in the tumor microenvironment using a STING agonist results in the engagement of innate and adaptive immune signaling and impairs the growth of KEAP1-mutant tumors. Our results suggest that targeting PARP and STING pathways, individually or in combination, represents a therapeutic strategy in NSCLC patients harboring alterations in KEAP1.
Keywords: BRCAness; EMSY; KEAP1; NSCLC; PARP inhibitors; STING agonsts; immune evasion; interferon; lung cancer; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests T.P. has received Honoraria/Consulting fees from Calithera Biosciences and Vividion Therapeutics and research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Dracen Pharmaceuticals, and Agios Pharmaceuticals. M.P. is a cofounder of Coho Therapeutics. He is also a consultant for, a member of the scientific advisory board of, and has financial interests in Coho Therapeutics, CullGen, Kymera Therapeutics, Santi Therapeutics, and SEED Therapeutics. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Bagaev A, Kotlov N, Nomie K, Svekolkin V, Gafurov A, Isaeva O, Osokin N, Kozlov I, Frenkel F, Gancharova O, et al. (2021). Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 39, 845–865 e847. - PubMed
-
- Bar J, Herbst RS, and Onn A (2008). Multitargeted inhibitors in lung cancer: new clinical data. Clin Lung Cancer 9 Suppl 3, S92–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

