Integration of transcriptome and proteome profiles in placenta accreta reveals trophoblast over-migration as the underlying pathogenesis
- PMID: 34963445
- PMCID: PMC8903580
- DOI: 10.1186/s12014-021-09336-8
Integration of transcriptome and proteome profiles in placenta accreta reveals trophoblast over-migration as the underlying pathogenesis
Abstract
Background: Placenta accreta (PA) is a major cause of maternal morbidity and mortality in modern obstetrics, few studies have explored the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Methods: In our study, transcriptome and proteome profiling were performed in placental tissues from ten participants including five cases each in the PA and control groups to clarify the pathogenesis of PA.
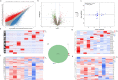
Results: We identified differential expression of 37,743 transcripts and 160 proteins between the PA and control groups with an overlap rate of 0.09%. The 33 most-significant transcripts and proteins were found and further screened and analyzed. Adhesion-related signature, chemotaxis related signatures and immune related signature were found in the PA group and played a certain role. Sum up two points, three significant indicators, methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2 (MeCP2), podocin (PODN), and apolipoprotein D (ApoD), which participate in "negative regulation of cell migration", were downregulated at the mRNA and protein levels in PA group. Furthermore, transwell migration and invasion assay of HTR-8/SVneo cell indicated the all of them impaired the migration and invasion of trophoblast.
Conclusion: A poor correlation was observed between the transcriptome and proteome data and MeCP2, PODN, and ApoD decreased in transcriptome and proteome profiling, resulting in increased migration of trophoblasts in the PA group, which clarify the mechanism of PA and might be the biomarkers or therapy targets in the future.
Keywords: Migration; Placenta accreta; Proteome; Transcriptome; Trophoblast.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Jauniaux E, Collins S, Burton GJ. Placenta accreta spectrum: pathophysiology and evidence-based anatomy for prenatal ultrasound imaging. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(1):75–87. - PubMed
-
- Jauniaux E, Jurkovic D. Placenta accreta: pathogenesis of a 20th century iatrogenic uterine disease. Placenta. 2012;33(4):244–251. - PubMed
-
- Thurn L, Lindqvist PG, Jakobsson M, Colmorn LB, Klungsoyr K, Bjarnadóttir RI, et al. Abnormally invasive placenta-prevalence, risk factors and antenatal suspicion: results from a large population-based pregnancy cohort study in the Nordic countries. BJOG. 2016;123(8):1348–55. - PubMed
-
- Qi WH, Zheng MY, Li C, Xu L, Xu JE. Screening of differential proteins of placenta tissues in patients with pre-eclampsia by iTRAQ proteomics techniques. Minerva Med. 2017;108(5):389–395. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
