Fit Factor Change on Quantitative Fit Testing of Duckbill N95 Respirators with the Use of Safety Goggles
- PMID: 34963714
- PMCID: PMC8664035
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23972
Fit Factor Change on Quantitative Fit Testing of Duckbill N95 Respirators with the Use of Safety Goggles
Abstract
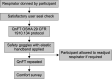
N95 respirators and safety goggles are important components of personal protective equipment to reduce the spread of airborne infections, such as COVID-19, among healthcare workers. Poor N95 respirator seal may reduce its protective effect, thereby increasing transmission. Quantitative fit testing is an established way of assessing the N95 respirator fit, which provides a quantitative measure for seal, called the fit factor. Duckbill N95 respirators frequently fail the fit test. We hypothesized that using safety goggles with a wraparound elastic headband will increase their fit-factor by reinforcing the seal between the face and the upper margin of the respirator. We studied the effect of safety goggles with a wraparound elastic headband (3M™ Chemical Splash Resistant Goggles, ID 70006982741) on the fit factor of two types of Duckbill N95 respirators (Halyard FLUIDSHIELD*3, Model 99SA070M, and ProShield® N95 Model TN01-11) in 63 healthy volunteers in a nonrandomized, before-and-after intervention study design. The mean fit factor increased from 69.4 to 169.1 increased from 17/63 (27%) to 46/63 (73%) after the intervention (p <0.0001, OR 3 [95% CI = 4.9-1223]). This is the first study to explore the impact of safety goggles on N95 respirator fit. We conclude that the use of safety goggles with a wraparound elastic headband increases the fit factor of the tested Duckbill N95 respirators.
How to cite this article: Johns M, Kyaw S, Lim R, Stewart WC, Thambiraj SR, Shehabi Y, et al. Fit Factor Change on Quantitative Fit Testing of Duckbill N95 Respirators with the Use of Safety Goggles. Indian J Crit Care Med 2021;25(9):981-986.
Keywords: Eyeglasses; HCW (Healthcare workers); Infectious diseases; Intensive care; N95 MASK; N95 respirators; Occupational injury; Personal protective equipment; Safety.
Copyright © 2021; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: Dr Arora is the Director of Quiz Time in Critical Care Pty Ltd, Sydney, Australia; which runs the website www.gotheextramile.com - MCQ in Critical Care. Dr Arora is not paid any salary for his work with Go the Extra Mile.
Figures



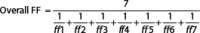

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
