Predictive Biomarkers of Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with IFNα ± Bevacizumab: Results from CALGB 90206 (Alliance)
- PMID: 34965953
- PMCID: PMC9240110
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-2386
Predictive Biomarkers of Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with IFNα ± Bevacizumab: Results from CALGB 90206 (Alliance)
Abstract
Purpose: CALGB 90206 was a phase III trial of 732 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) comparing bevacizumab plus IFNα (BEV + IFN) with IFNα alone (IFN). No difference in overall survival (OS) was observed. Baseline samples were analyzed to identify predictive biomarkers for survival benefit.
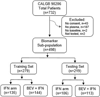
Patients and methods: A total of 32 biomarkers were assessed in 498 consenting patients randomly assigned into training (n = 279) and testing (n = 219) sets. The proportional hazards model was used to test for treatment arm and biomarker interactions of OS. The estimated coefficients from the training set were used to compute a risk score for each patient and to classify patients by risk in the testing set. The resulting model was assessed for predictive accuracy using the time-dependent area under the ROC curve (tAUROC).
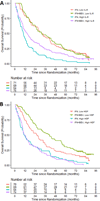
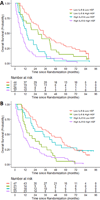
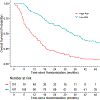
Results: A statistically significant three-way interaction between IL6, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and bevacizumab treatment was observed in the training set and confirmed in the testing set (P < 0.0001). The model based on IL6, HGF, and bevacizumab treatment was predictive of OS (P < 0.001), with the high- and low-risk groups having a median OS of 10.2 [95% confidence interval (CI), 8.0-13.8] and 34.3 (95% CI, 28.5-40.5) months, respectively. The average tAUROC for the final model of OS based on 100 randomly split testing sets was 0.78 (first, third quartiles = 0.77, 0.79).
Conclusions: IL6 and HGF are potential predictive biomarkers of OS benefit from BEV + IFN in patients with mRCC. The model based on key biological and clinical factors demonstrated predictive efficacy for OS. These markers warrant further validation in future anti-VEGF and immunotherapy in mRCC trials. See related commentaries by Mishkin and Kohn, p. 2722 and George and Bertagnolli, p. 2725.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00072046.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Linking Genotype to Phenotype: Bench to Bedside.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 1;28(13):2725-2727. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0027. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35467726
-
Biomarker Development: Bedside to Bench.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 1;28(13):2722-2724. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0750. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35481871
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

