Predicting Pseudogene-miRNA Associations Based on Feature Fusion and Graph Auto-Encoder
- PMID: 34966413
- PMCID: PMC8710693
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.781277
Predicting Pseudogene-miRNA Associations Based on Feature Fusion and Graph Auto-Encoder
Abstract
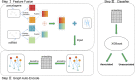
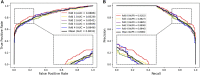
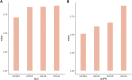
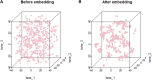
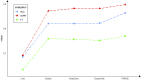
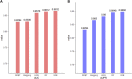
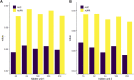
Pseudogenes were originally regarded as non-functional components scattered in the genome during evolution. Recent studies have shown that pseudogenes can be transcribed into long non-coding RNA and play a key role at multiple functional levels in different physiological and pathological processes. microRNAs (miRNAs) are a type of non-coding RNA, which plays important regulatory roles in cells. Numerous studies have shown that pseudogenes and miRNAs have interactions and form a ceRNA network with mRNA to regulate biological processes and involve diseases. Exploring the associations of pseudogenes and miRNAs will facilitate the clinical diagnosis of some diseases. Here, we propose a prediction model PMGAE (Pseudogene-MiRNA association prediction based on the Graph Auto-Encoder), which incorporates feature fusion, graph auto-encoder (GAE), and eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). First, we calculated three types of similarities including Jaccard similarity, cosine similarity, and Pearson similarity between nodes based on the biological characteristics of pseudogenes and miRNAs. Subsequently, we fused the above similarities to construct a similarity profile as the initial representation features for nodes. Then, we aggregated the similarity profiles and associations of nodes to obtain the low-dimensional representation vector of nodes through a GAE. In the last step, we fed these representation vectors into an XGBoost classifier to predict new pseudogene-miRNA associations (PMAs). The results of five-fold cross validation show that PMGAE achieves a mean AUC of 0.8634 and mean AUPR of 0.8966. Case studies further substantiated the reliability of PMGAE for mining PMAs and the study of endogenous RNA networks in relation to diseases.
Keywords: ceRNA network; extreme gradient boosting; feature fusion; graph auto-encoder; microRNA; pseudogene.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Sun, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inferring pseudogene-MiRNA associations based on an ensemble learning framework with similarity kernel fusion.Sci Rep. 2023 May 31;13(1):8833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36054-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37258695 Free PMC article.
-
A graph auto-encoder model for miRNA-disease associations prediction.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa240. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa240. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34293850
-
Predicting miRNA-Disease Associations Based On Multi-View Variational Graph Auto-Encoder With Matrix Factorization.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022 Jan;26(1):446-457. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3088342. Epub 2022 Jan 17. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022. PMID: 34111017
-
Pseudogene-Derived lncRNAs and Their miRNA Sponging Mechanism in Human Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 28;8:85. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00085. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32185172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The biological functions and regulations of competing endogenous RNA].Yi Chuan. 2015 Aug;37(8):756-64. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-073. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 26266779 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
MIFAM-DTI: a drug-target interactions predicting model based on multi-source information fusion and attention mechanism.Front Genet. 2024 May 6;15:1381997. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1381997. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38770418 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring pseudogene-MiRNA associations based on an ensemble learning framework with similarity kernel fusion.Sci Rep. 2023 May 31;13(1):8833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36054-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37258695 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomic study of common sellar region lesions differentiation in magnetic resonance imaging based on multi-classification machine learning model.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 May 3;25(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01690-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40319246 Free PMC article.
-
MDFGNN-SMMA: prediction of potential small molecule-miRNA associations based on multi-source data fusion and graph neural networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jan 13;26(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06040-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 39806287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldi P. (2012). Autoencoders, Unsupervised Learning, and Deep Architectures. Bellevue, WA: ICML Unsupervised and Transfer Learning, 37–49.
-
- Cao S., Lu W., Xu Q. (2015). “GraRep: Learning Graph Representations with Global Structural Information,” in Proceedings of the 24th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, 891–900.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

