Network Pharmacology Study on Molecular Mechanisms of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
- PMID: 34966435
- PMCID: PMC8712121
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3574321
Network Pharmacology Study on Molecular Mechanisms of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
Background: Coronary heart disease is characterized by the formation of arterial plaque. If not taken seriously, it will cause serious consequences such as myocardial infarction and heart failure. Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction first appeared in "Synopsis of Prescriptions of the Golden Chamber" and is a representative prescription for the treatment of coronary heart disease. This study aims to explain the mechanism of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in the treatment of coronary heart disease through network pharmacology and clinical trials.
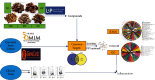
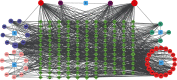
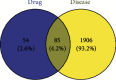
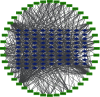
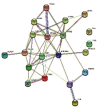
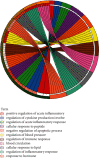
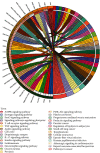
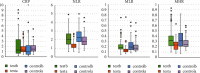
Methods: We first identified the core compounds of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction and their potential targets through TCMSP. Then, We analyzed the molecular targets of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction in coronary heart disease with OMIM and GeneCards databases. After the common targets were screened out, we manage to figure out the pathways of these target genes through STRING. Finally, we verify the treatment results in clinical trials.
Results: Through network pharmacology analysis, we discovered that several core compounds of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction have anti-inflammatory effects and are of great significance to treatment of cardiovascular diseases. The mechanism may be closely related to PPARγ, inflammation, TNF signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Clinical trials have also proved the key role of inflammation.
Conclusions: Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction may play a role in treating coronary heart disease by activating PPARγ. TNF signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway are potential mechanisms as well. The application of network pharmacology can provide a novel method for the research of Chinese herbal medicine. We hope that Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction will be recognized as a complementary or alternative treatment for coronary heart disease.
Copyright © 2021 Jin Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Zhishi Xiebai Guizhi Decoction on phenotypic transformation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Oct;49(19):5297-5306. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240611.703. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39701768 Chinese.
-
Exploring the Mechanism of Zhishi-Xiebai-Guizhi Decoction for the Treatment of Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Analyses.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(26):2059-2074. doi: 10.2174/0113816128293601240523063527. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38867532
-
Five-layer-funnel filtering mode discovers effective components of Chinese medicine formulas: Zhishi-Xiebai-Guizhi decoction as a case study.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155678. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155678. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38754214
-
[Connotation of deficiency-induced chest impediment and Renshen Decoction based on severe cases and modern pathophysiological mechanisms and its application in treatment of coronary heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, heart failure, hypotension, pulmonary arterial hypertension, and other critical illnesses].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Mar;50(6):1706-1714. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241106.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350958 Review. Chinese.
-
[Coronary heart disease: innovative understanding from traditional Chinese medicine and treatment by classic formulas].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;49(13):3684-3692. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240326.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39041141 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Investigate the Mechanism of Qushi Huatan Decoction Against Coronary Heart Disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Sep 11;18:4033-4049. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S463054. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39280256 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine on COVID-19 and Cardiac Injury: Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023 Sep 22;16:2863-2872. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S424078. eCollection 2023. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2023. PMID: 37771609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet (London, England) . 2015;385(9963):117–171. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

