New Metabolic, Digestive, and Oxidative Stress-Related Manifestations Associated with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
- PMID: 34966477
- PMCID: PMC8712172
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5599265
New Metabolic, Digestive, and Oxidative Stress-Related Manifestations Associated with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Abstract
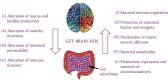
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) represents a pressing and generally invalidating syndrome that is triggered by a terrifying or stressful experience, relying on recurrently reliving the traumatic event feelings associated to it, which is subsequently linked to ongoing activations of stress-related neurobiological pathways and is often associated with neurodegeneration. In this paper, we examine what lies beneath this disorder, reviewing evidence that connects PTSD with a wide array of mechanisms and its intertwined pathways that can lead to the decompensation of different pathologies, such as cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal ailments, autoimmune disorders, and endocrine diseases. Also, the significance of the oxidative stress in this frame of reference is debated. Thus, knowing and identifying the main features of the distressing experience, the circumstances around it, as well as the neuropsychological and emotional characteristics of people prone to develop PTSD after going through disturbing incidents can offer an opportunity to anticipate the development of potential destructive consequences in several psychological dimensions: cognitive, affective, relational, behavioral, and somatic. We can also observe more closely the intricate connections of the disorder to other pathologies and their underlying mechanisms such as inflammation, oxidative stress, bacterial overgrowth syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, metabolic disorders, oxytocin, and cortisol in order to understand it better and to optimize the course of treatment and its management. The complex foundation PTSD possesses is supported by the existing clinical, preclinical, and experimental data encompassed in the current review. Different biological systems and processes such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, sympathetic nervous system, oxidative stress, inflammation, and microbiome suffer modifications and changes when it comes to PTSD; that is why targeted therapies exert tremendous alleviations of symptoms in patients diagnosed with this disorder. Therefore, this implies that PTSD is not restricted to the psychiatric domain and should be viewed as a systemic condition.
Copyright © 2021 Bianca Augusta Oroian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dohrenwend B. S., Dohrenwend B. P. Stressful Life Events: Their Nature and Effects . John Wiley & Sons; 1974.
-
- Selye H. The stress of life . McGraw-Hill Education; 1984.
-
- Lazarus R. S., Folkman S. Stress, Appraisal and Coping . New York: Springer; 1984.
-
- Bodenmann G., Randall A. K. The role of stress on close relationships and marital satisfaction. Clinical Psychology Review . 2009;29(2):105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical