EZH2 suppresses endogenous retroviruses and an interferon response in cancers
- PMID: 34966479
- PMCID: PMC8711646
- DOI: 10.18632/genesandcancer.218
EZH2 suppresses endogenous retroviruses and an interferon response in cancers
Abstract
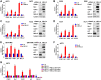
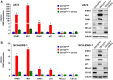
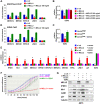
Ewing sarcoma is an aggressive cancer of bone and soft tissue in children. It is characterized by the chromosomal translocation between EWS and an Ets family transcription factor, most commonly FLI1. We recently reported that Ewing sarcoma depends on the autocrine signaling mediated by a cytokine, NELL2. NELL2 signaling stimulates the transcriptional output of EWS-FLI1 through the BAF chromatin remodeling complexes. While studying the impact of NELL2 silencing on Ewing sarcoma, we found that suppression of NELL2 signaling induces the expression of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) and LINE-1 retrotransposons, an interferon response, and growth arrest. We determined that a histone methyltransferase, EZH2, is the critical downstream target of NELL2 signaling in suppressing ERVs, LINE-1, an interferon response, and growth arrest. We show that EZH2 inhibitors induce ERVs, LINE-1, and an interferon response in a variety of cancer types. These results uncover the role for NELL2-EZH2 signaling in suppressing endogenous virus-like agents and an antiviral response, and suggest the potential utility of EZH2 inhibitors in enhancing anti-tumor immunity.
Keywords: EZH2; Ewing sarcoma; NELL2; endogenous retroviruses; interferon response.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Slit2 signaling stimulates Ewing sarcoma growth.Genes Cancer. 2022 Dec 14;13:88-99. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.227. eCollection 2022. Genes Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36533189 Free PMC article.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors suppress EWS-FLI1-dependent transcription and the IGF1 autocrine mechanism in Ewing sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43504-43517. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9762. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27259270 Free PMC article.
-
EWS-FLI1-mediated suppression of the RAS-antagonist Sprouty 1 (SPRY1) confers aggressiveness to Ewing sarcoma.Oncogene. 2017 Feb 9;36(6):766-776. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.244. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27375017
-
Therapeutic opportunities in Ewing sarcoma: EWS-FLI inhibition via LSD1 targeting.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):17616-30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7124. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EWS/FLI1 Target Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Ewing Sarcoma.Front Oncol. 2015 Jul 20;5:162. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00162. eCollection 2015. Front Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26258070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retinoblastoma Cell Growth In Vitro and Tumor Formation In Ovo-Influence of Different Culture Conditions.Methods Protoc. 2022 Mar 2;5(2):21. doi: 10.3390/mps5020021. Methods Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35314658 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite repeat RNA expression in epithelial ovarian cancer associates with a tumor-immunosuppressive phenotype.J Clin Invest. 2022 Aug 15;132(16):e155931. doi: 10.1172/JCI155931. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35708912 Free PMC article.
-
PRC2-Mediated Epigenetic Suppression of Type I IFN-STAT2 Signaling Impairs Antitumor Immunity in Luminal Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2022 Dec 16;82(24):4624-4640. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0736. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36222718 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation in Primary CNS Tumors: An Opportunity to Bridge Old and New WHO Classifications.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;15(9):2511. doi: 10.3390/cancers15092511. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37173979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 in Oncology.Cancer Treat Res. 2023;190:273-320. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-45654-1_9. Cancer Treat Res. 2023. PMID: 38113005
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

