Humeral Shaft Fracture Sustained During Arm Wrestling with Review of Factors Contributing to its Causation
- PMID: 34966490
- PMCID: PMC8667248
- DOI: 10.5704/MOJ.2111.003
Humeral Shaft Fracture Sustained During Arm Wrestling with Review of Factors Contributing to its Causation
Abstract
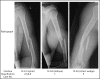
Introduction: Humeral shaft fractures are the most common injury sustained in arm wrestling, and its various biomechanical, anatomical, kinematic and electromyographic aspects have been studied and reported. We present a series of six cases of humeral shaft fractures in the arm wrestlers and a review of basic science studies to determine the factors contributing to their causation.
Materials and methods: Six humeral shaft fractures associated with arm wrestling were treated between December 2018 and January 2020. The medical records and radiographs were retrospectively reviewed. In addition, the characteristics of the patients, their opponents, and the fractures were noted in a pre-designed data sheet.
Results: There were six men with an average age of 27.5 years (SD ± 8.9). All were amateurs who were occasional arm wrestlers. Three fractures each were sustained in the sitting and standing position, four in the losing phase, one in the winning phase, and one in the stalling phase. The dominant side humerus was involved in all but one case. The fracture types were 12-A1 (n=4); 12-B1 (n=1); 12-A2 (n=1). Three fractures were treated by open reduction and internal fixation, while three were treated conservatively with satisfactory healing.
Conclusion: Humeral shaft fractures in arm wrestling are common in amateurs. There is no association of the fracture with the position of the players or the phase of the match. However, arm wrestlers should be aware of this complication and should receive proper guidance to reduce the risk of humeral shaft fractures.
Keywords: arm wrestling; biomechanics; electromyography; humeral fracture.
© 2021 Malaysian Orthopaedic Association (MOA). All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Frankowska-Rutkowska M, Gorska J, Jedwabinski M, Matewski D, Maciejewski M.. Fracture of the humerus during arm wrestling: Report of 9 cases and review of literature. Med Biol Sciences. 2013;27(3):36–8. doi: 10.12775/MBS-2013-0022. doi: - DOI
-
- Correia RF, Ribeiro AN, de Araujo RP. Arm-wrestling injuries – A systematic review of the medical literature. Man Ther, Posturology Rehabil J. 2018. pp. 1–3. doi: - DOI
-
- Wahab FA. Engaging armwrestling interest with Brunei Armwrestling Association. December 14th, 2019. https://sutera.co/engaging-armwrestling-interest-with-brunei-armwrestlin... (accessed on 25 March 2020)
-
- Moon MS, Kim I, Han IH, Suh KH, Hwang JD. Arm wrestler’s injury: Report of seven cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980. pp. 219–21. 147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources