Co-treatment with miR-21-5p inhibitor and Aurora kinase inhibitor reversine suppresses breast cancer progression by targeting sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 2
- PMID: 34967265
- PMCID: PMC8805969
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009410
Co-treatment with miR-21-5p inhibitor and Aurora kinase inhibitor reversine suppresses breast cancer progression by targeting sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 2
Abstract
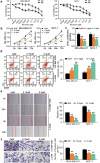
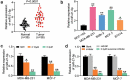
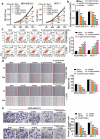
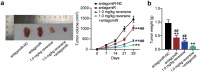
Numerous studies have reported the regulatory effects of miR-21-5p and reversine in human breast cancer (HBC). However, the mechanism of reversine and miR-21-5p has not been fully investigated in HBC. The aim of the current study was to assess the mechanism of action of reversine, with or without miR-21-5p, in HBC progression. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot results confirmed the upregulation of miR-21-5p and downregulation of sprouty RTK signaling antagonist 2 (SPRY2) in HBC. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase assay identified the correlation between miR-21-5p and SPRY2. Cell function experiment results indicated a decrease in migration, proliferation, and invasion of HBC cells treated with miR-21-5p inhibitor and reversine; however, an increase in apoptosis was observed in these cells. Apoptotic ability was more enhanced and migration, proliferation, and invasion were more impaired in HBC cells treated with both miR-21-5p inhibitor and reversine than in those treated individually with either inhibitors. SPRY2, downstream of miR-21-5p, participated in HBC progression with reversine. Overall, our study proved that combining the miR-21-5p inhibitor with reversine produced a synergistic effect by regulating SPRY2, thereby limiting HBC progression. This knowledge might offer insights into the clinical therapy of HBC.
Keywords: Human breast cancer; SPRY2; miR-21-5p; reversine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crocin suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation by down-regulating tumor promoter miR-122-5p and up-regulating tumor suppressors FOXP2 and SPRY2.Environ Toxicol. 2023 Jul;38(7):1597-1608. doi: 10.1002/tox.23789. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Environ Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36988377
-
Downregulation of Sprouty homolog 2 by microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and invasion, however promotes the apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):1810-6. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3567. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25825239 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of microRNA-660-5p decreases breast cancer progression through direct targeting of TMEM41B.Hereditas. 2024 Dec 21;161(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s41065-024-00357-5. Hereditas. 2024. PMID: 39709500 Free PMC article.
-
miR-424-5p regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting doublecortin-like kinase 1 in basal-like breast cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jun;102:147-152. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.018. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29550638
-
MicroRNA-99a-5p suppresses breast cancer progression and cell-cycle pathway through downregulating CDC25A.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Apr;234(4):3526-3537. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26906. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30443946
Cited by
-
Transcription factor STAT4 counteracts radiotherapy resistance in breast carcinoma cells by activating the MALAT1/miR-21-5p/THRB regulatory network.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 15;14(4):1501-1522. doi: 10.62347/VSJU7227. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38726265 Free PMC article.
-
Reversine inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells through targeting MEK1.J Bone Oncol. 2024 Apr 17;46:100601. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2024.100601. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Bone Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38706714 Free PMC article.
-
Text Mining Strategy Identifies Gene Networks Under Control of miR-21 in Breast Cancer Development.Cancer Med. 2025 Jul;14(13):e70986. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70986. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40567015 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the intricate relationship between miRNA dysregulation and breast cancer development: insights into the impact of environmental chemicals.Front Immunol. 2024 May 14;15:1333563. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1333563. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38807590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Defined PANoptosis-Related miRNA Signature for Predicting the Prognosis and Immune Characteristics in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A miRNA Signature for the Prognosis of ccRCC.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 28;24(11):9392. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119392. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(8):1941–1953. - PubMed
-
- Bernard-Marty C, Cardoso F, Piccart MJ.. Facts and controversies in systemic treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 2004;9(6):617–632. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Goding Sauer A, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(6):439–448. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):52–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
