Reexamining assumptions about miRNA-guided gene silencing
- PMID: 34967419
- PMCID: PMC8789053
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab1256
Reexamining assumptions about miRNA-guided gene silencing
Abstract
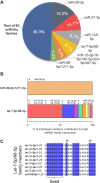
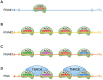
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short endogenously expressed RNAs that have the potential to regulate the expression of any RNA. This potential has led to the publication of several thousand papers each year connecting miRNAs to many different genes and human diseases. By contrast, relatively few papers appear that investigate the molecular mechanism used by miRNAs. There is a disconnect between rigorous understanding of mechanism and the extraordinary diversity of reported roles for miRNAs. Consequences of this disconnect include confusion about the assumptions underlying the basic science of human miRNAs and slow development of therapeutics that target miRNAs. Here, we present an overview of investigations into miRNAs and their impact on gene expression. Progress in our understanding of miRNAs would be aided by a greater focus on the mechanism of miRNAs and a higher burden of evidence on researchers who seek to link expression of a particular miRNA to a biological phenotype.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures







References
-
- Treiber T., Treiber N., Meister G.. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019; 20:5–20. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee D., Slack F.. Control of developmental timing by small temporal RNAs: a paradigm for RNA-mediated regulation of gene expression. Bioessays. 2002; 24:119–129. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli A.E., Ruvkun G.. Control of developmental timing by micrornas and their targets. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002; 18:495–513. - PubMed
-
- Lee R.C., Feinbaum R.L., Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; 75:843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

