Genomic analyses reveal range-wide devastation of sea otter populations
- PMID: 34967471
- PMCID: PMC9875727
- DOI: 10.1111/mec.16334
Genomic analyses reveal range-wide devastation of sea otter populations
Abstract
The genetic consequences of species-wide declines are rarely quantified because the timing and extent of the decline varies across the species' range. The sea otter (Enhydra lutris) is a unique model in this regard. Their dramatic decline from thousands to fewer than 100 individuals per population occurred range-wide and nearly simultaneously due to the 18th-19th century fur trade. Consequently, each sea otter population represents an independent natural experiment of recovery after extreme population decline. We designed sequence capture probes for 50 Mb of sea otter exonic and neutral genomic regions. We sequenced 107 sea otters from five populations that span the species range to high coverage (18-76×) and three historical Californian samples from ~1500 and ~200 years ago to low coverage (1.5-3.5×). We observe distinct population structure and find that sea otters in California are the last survivors of a divergent lineage isolated for thousands of years and therefore warrant special conservation concern. We detect signals of extreme population decline in every surviving sea otter population and use this demographic history to design forward-in-time simulations of coding sequence. Our simulations indicate that this decline could lower the fitness of recovering populations for generations. However, the simulations also demonstrate how historically low effective population sizes prior to the fur trade may have mitigated the effects of population decline on genetic health. Our comprehensive approach shows how demographic inference from genomic data, coupled with simulations, allows assessment of extinction risk and different models of recovery.
Keywords: conservation genomics; demographic simulations; genetic load; population bottleneck; sea otters.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



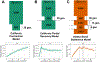


Comment in
-
Disentangling the genetic consequences of demographic change.Mol Ecol. 2023 Jan;32(2):278-280. doi: 10.1111/mec.16798. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Mol Ecol. 2023. PMID: 36440474
References
-
- Aguilar A, Jessup DA, Estes J, & Garza JC (2008). The distribution of nuclear genetic variation and historical demography of sea otters. Animal Conservation, 11(1), 35–45. 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2007.00144.x - DOI
-
- Allentoft ME, Sikora M, Sjögren K-G, Rasmussen S, Rasmussen M, Stenderup J, Damgaard PB, Schroeder H, Ahlström T, Vinner L, Malaspinas A-S, Margaryan A, Higham T, Chivall D, Lynnerup N, Harvig L, Baron J, Casa PD, Dąbrowski P, … Willerslev E (2015). Population genomics of Bronze Age Eurasia. Nature, 522(7555), 167–172. 10.1038/nature14507 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ballachey BE, Bodkin JL, & DeGange AR (1994). An overview of sea otter studies. Marine Mammals and the Exxon Valdez, 47–59.
-
- Beichman AC, Koepfli K-P, Li G, Murphy W, Dobrynin P, Kliver S, Tinker MT, Murray MJ, Johnson J, Lindblad-Toh K, Karlsson EK, Lohmueller KE, & Wayne RK (2019). Aquatic adaptation and depleted diversity: A deep dive into the genomes of the sea otter and giant otter. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 36(12), 2631–2655. 10.1093/molbev/msz101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

