Genomic Understanding Reveals the Important Role of FGFR2 as Paeoniflorin Target for Circumventing Breast Cancer Resistance to Tamoxifen
- PMID: 34967576
- PMCID: PMC9080378
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.12.3949
Genomic Understanding Reveals the Important Role of FGFR2 as Paeoniflorin Target for Circumventing Breast Cancer Resistance to Tamoxifen
Abstract
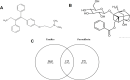
Objectives: Paeoniflorin (PF), a compound found in Paeonia lactiflora and Paeonia suffruticosa, has anticancer potential, particularly in inhibiting migration and invasion, the resistant cancer cells hallmarks. To date, the mechanism of overcoming tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer is not yet elucidated. This research aims to explore the potential target of PF as a co-treatment for circumventing breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen with a genomic understanding-bioinformatics.
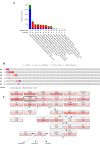
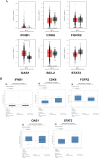
Methods: Microarray data originating from GSE67916 and GSE85871 in the NCBI GEO database was analyzed to obtain differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Further analyses were performed on DEGs using the DAVID v6.8, STRING-DB v11.0, the Cytoscape, and cBioportal. Gene expression analysis validation in breast cancer cells and tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells was accomplished using GEPIA and ONCOMINE databases. Survival rate analysis of selected genes was conducted using Kaplan-Meier.
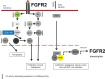
Results: We obtained 175 DEGs from the two samples (tamoxifen-resistant and paeoniflorin-treated). DEG involves in 70 biological processes, 26 cellular components, and 18 molecular functions, and three pathways relevant to breast cancer. The PPI network analysis and hub genes selection obtained 10 genes with the highest degree scores. Genetic changes for selected genes, including IFNB1, CDK6, FGFR2, OAS1, BCL2, and STAT2 were found from 0.5% to 7% of the case population per patient case. Additional analysis using cBioportal revealed FGFR signaling pathway through Ras is important for the PF mechanism in circumventing breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen. ONCOMINE and GEPIA analysis emphasized the importance of selected genes in the tamoxifen-resistance mechanism.
Conclusion: PF has potential to be used as a co-treatment for circumventing breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen by targeting FGFR2 signaling, but further validation is needed.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Paeoniflorin; breast cancer; tamoxifen resistance.
Figures



References
-
- Chambard JC, Lefloch R, Pouysségur J, Lenormand P. ERK implication in cell cycle regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1299–310. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

