Effects of Simulated Microgravity and Hypergravity Conditions on Arm Movements in Normogravity
- PMID: 34970122
- PMCID: PMC8712641
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2021.750176
Effects of Simulated Microgravity and Hypergravity Conditions on Arm Movements in Normogravity
Abstract
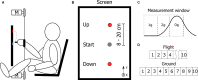
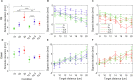
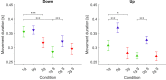
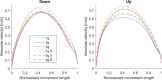
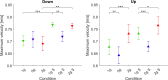
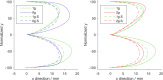
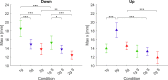
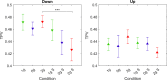
The human sensorimotor control has evolved in the Earth's environment where all movement is influenced by the gravitational force. Changes in this environmental force can severely impact the performance of arm movements which can be detrimental in completing certain tasks such as piloting or controlling complex vehicles. For this reason, subjects that are required to perform such tasks undergo extensive training procedures in order to minimize the chances of failure. We investigated whether local gravity simulation of altered gravitational conditions on the arm would lead to changes in kinematic parameters comparable to the full-body experience of microgravity and hypergravity onboard a parabolic flight. To see if this would be a feasible approach for on-ground training of arm reaching movements in altered gravity conditions we developed a robotic device that was able to apply forces at the wrist in order to simulate micro- or hypergravity conditions for the arm while subjects performed pointing movements on a touch screen. We analyzed and compared the results of several kinematic parameters along with muscle activity using this system with data of the same subjects being fully exposed to microgravity and hypergravity conditions on a parabolic flight. Both in our simulation and in-flight, we observed a significant increase in movement durations in microgravity conditions and increased velocities in hypergravity for upward movements. Additionally, we noted a reduced accuracy of pointing both in-flight and in our simulation. These promising results suggest, that locally simulated altered gravity can elicit similar changes in some movement characteristics for arm reaching movements. This could potentially be exploited as a means of developing devices such as exoskeletons to aid in training individuals prior to undertaking tasks in changed gravitational conditions.
Keywords: arm kinematics; exoskeletons; hypergravity; microgravity; parabolic flight; robot assisted training.
Copyright © 2021 Jamšek, Kunavar, Blohm, Nozaki, Papaxanthis, White and Babič.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Artiles A. D., Schor D., Clément G. (2018). “Effects of inverted vision on hand-pointing performance in altered gravity during parabolic flight,” in IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, (Big Sky, MT, USA: IEEE Computer Society; ), 1–9. 10.1109/AERO.2018.8396370 - DOI
-
- Berger M., Mescheriakov S., Molokanova E., Lechner-Steinleitner S., Seguer N., Kozlovskaya I. (1997). Pointing arm movements in short- and long-term spaceflights. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 68, 781–787. - PubMed
-
- Bock O., Arnold K. E., Cheung B. S. K. (1996). Performance of a simple aiming task in hypergravity: II. Detailed response characteristics. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 67, 133–138. - PubMed
-
- Bock O., Howard I. P., Money K. E., Arnold K. E. (1992). Accuracy of aimed arm movements in changed gravity. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 63, 994–998. - PubMed
-
- Bolender H., Stevenin H., Bessone L., Torres A. (2006). Preparing for space. Eur. Space Agency Bull. 128, 32–40. Available online at: https://www.esa.int/esapub/bulletin/bulletin128/bulletin128.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

