Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill Regulates the Bone Immune Microenvironment via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Vitro
- PMID: 34970139
- PMCID: PMC8712765
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.746786
Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill Regulates the Bone Immune Microenvironment via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Vitro
Abstract
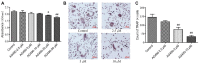
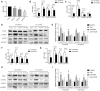
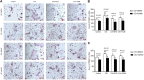
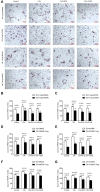
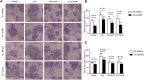
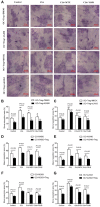
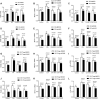
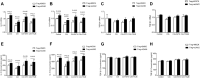
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by an impaired articular bone immune microenvironment, which is associated with regulatory T cells (Tregs) hypofunction and osteoclasts (OCs) hyperfunction and leads to articular bone erosion and systemic bone loss. Studies have shown that Tregs slow bone loss in RA by regulating the bone resorption function of OCs and the JAK/STAT signaling pathway can regulate the immunosuppressive function of Tregs and reduce the bone erosion function of OCs. Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill (YSJB) is a classic Chinese herbal compound for the treatment of RA. However, whether YSJB regulates bone immune microenvironment homeostasis through JAK/STAT signaling pathway remains unclear. Based on in vitro OC single culture, Treg single culture and OC-Treg coculture systems, treatments were performed using drug-containing serum, AG490 and JAK2 siRNA to explore whether YSJB-containing serum regulates the homeostasis of the bone immune microenvironment through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. In vitro, YSJB treatment decreased the number of TRAP+ cells and the areas of bone resorption and inhibited the expression of RANK, NFATc1, c-fos, JAK2, and STAT3 in both the OC single culture system and the OC-Treg coculture system. Tregs further reduced the number of TRAP+ cells and the areas of bone resorption in the coculture system. YSJB promoted the secretion of IL-10 while inhibiting the expression of JAK2 and STAT3 in Tregs. Moreover, inhibiting the expression of JAK2 with the JAK2 inhibitor AG490 and JAK2 siRNA improved the immunosuppressive functions of Treg, inhibited OC differentiation and bone resorption. Our study demonstrates that YSJB can regulate OC-mediated bone resorption and Treg-mediated bone immunity through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. This study provides a new strategy for regulating the bone immune microenvironment in RA with traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway; Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill; osteoclast; regulatory T cell; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Xia, Fan, Li, Lu, Ye, Xi, Wang, Zhao and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adam S., Simon N., Steffen U., Andes F. T., Scholtysek C., Müller D. I. H., et al. (2020). JAK Inhibition Increases Bone Mass in Steady-State Conditions and Ameliorates Pathological Bone Loss by Stimulating Osteoblast Function. Sci. Transl. Med. 12 (530), eaay4447. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay4447 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bellido T., Borba V. Z., RobersonManolagas P. S. C., Manolagas S. C. (1997). Activation of the Janus Kinase/STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) Signal Transduction Pathway by Interleukin-6-type Cytokines Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation. Endocrinology 138 (9), 3666–3676. 10.1210/endo.138.9.5364 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

