Neuroprotection Against NMDA-Induced Retinal Damage by Philanthotoxin-343 Involves Reduced Nitrosative Stress
- PMID: 34970151
- PMCID: PMC8714026
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.798794
Neuroprotection Against NMDA-Induced Retinal Damage by Philanthotoxin-343 Involves Reduced Nitrosative Stress
Abstract
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) overstimulation is known to mediate neurodegeneration, and hence represents a relevant therapeutic target for neurodegenerative disorders including glaucoma. This study examined the neuroprotective effects of philanthotoxin (PhTX)-343 against NMDA-induced retinal injury in rats. Male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into three groups; group 1 received phosphate buffer saline as the negative control, group 2 was injected with NMDA (160 nM) to induce retinal excitotoxic injury, and group 3 was pre-treated with PhTX-343 (160 nM) 24 h before NMDA exposure. All treatments were given intravitreally and bilaterally. Seven days post-treatment, rats were subjected to visual behaviour assessments using open field and colour recognition tests. Rats were then euthanized, and the retinas were harvested and subjected to haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining for morphometric analysis and 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT) ELISA protocol as the nitrosative stress biomarker. PhTX-343 treatment prior to NMDA exposure improved the ability of rats to recognize visual cues and preserved visual functions (i.e., recognition of objects with different colours). Morphological examination of retinal tissues showed that the fractional ganglion cell layer thickness within the inner retina (IR) in the PhTX-343 treated group was greater by 1.28-fold as compared to NMDA-treated rats (p < 0.05) and was comparable to control rats (p > 0.05). Additionally, the number of retinal cell nuclei/100 μm2 in IR for the PhTX-343-treated group was greater by 1.82-fold compared to NMDA-treated rats (p < 0.05) and was comparable to control group (p > 0.05). PhTX-343 also reduced the retinal 3-NT levels by 1.74-fold compared to NMDA-treated rats (p < 0.05). In conclusion, PhTX-343 pretreatment protects against NMDA-induced retinal morphological changes and visual impairment by suppressing nitrosative stress as reflected by the reduced retinal 3-NT level.
Keywords: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor overstimulation; excitotoxicity; glaucoma; neurodegeneration; philanthotoxin-343; retinal ganglion cell; visual behavioural analysis.
Copyright © 2021 Mohamad, Abu, Fazel, Agarwal, Iezhitsa, Juliana, Mellor and Franzyk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

 and OB2;
and OB2; ) in the arena, and colour replacement phase (trial 4) where one blue object (OB1;
) in the arena, and colour replacement phase (trial 4) where one blue object (OB1; ) is replaced with a green object (OG;
) is replaced with a green object (OG; ). Rats were placed at the centre of the arena alone and allowed to explore freely, the rat’s movements were recorded using Any-maze software. OB1, object blue 1; OB2, object blue 2, OG, object green.
). Rats were placed at the centre of the arena alone and allowed to explore freely, the rat’s movements were recorded using Any-maze software. OB1, object blue 1; OB2, object blue 2, OG, object green.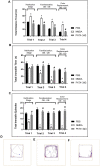
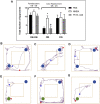
 and OB2;
and OB2; ), while during the colour replacement phase, one blue object (OB1;
), while during the colour replacement phase, one blue object (OB1; ) was replaced with a green object (OG;
) was replaced with a green object (OG; ). Representative track plots during familiarization stage for each group are shown in panel (B) PBS group, (C) NMDA group, and (D) PhTX-343 pre-treatment prior to NMDA exposure. Representative track plots during colour replacement phase for each group are shown in panel (E) PBS group, (F) NMDA group and (G) PhTX-343 pre-treatment group. *p < 0.05 vs PBS; #p < 0.05 vs NMDA. PBS, phosphate buffer saline; NMDA, N-methyl-
). Representative track plots during familiarization stage for each group are shown in panel (B) PBS group, (C) NMDA group, and (D) PhTX-343 pre-treatment prior to NMDA exposure. Representative track plots during colour replacement phase for each group are shown in panel (E) PBS group, (F) NMDA group and (G) PhTX-343 pre-treatment group. *p < 0.05 vs PBS; #p < 0.05 vs NMDA. PBS, phosphate buffer saline; NMDA, N-methyl-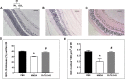

Similar articles
-
Philanthotoxin-343 attenuates retinal and optic nerve injury, and protects visual function in rats with N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced excitotoxicity.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 24;15(7):e0236450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236450. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32706792 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of magnesium acetyltaurate and taurine against NMDA-induced retinal damage involves reduced nitrosative stress.Mol Vis. 2018 Jul 25;24:495-508. eCollection 2018. Mol Vis. 2018. PMID: 30090013 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Magnesium Acetyltaurate Against NMDA-Induced Excitotoxicity in Rat Retina.Neurotox Res. 2017 Jan;31(1):31-45. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9658-9. Epub 2016 Aug 27. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 27568334
-
Antiapoptotic effect of taurine against NMDA-induced retinal excitotoxicity in rats.Neurotoxicology. 2019 Jan;70:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30385388
-
Neuroprotection by trans-resveratrol in rats with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced retinal injury: Insights into the role of adenosine A1 receptors.Neurosci Res. 2023 Aug;193:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Neurosci Res. 2023. PMID: 36796452
Cited by
-
Durable 3D murine ex vivo retina glaucoma models for optical coherence tomography.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Aug 2;14(9):4421-4438. doi: 10.1364/BOE.494271. eCollection 2023 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 37791268 Free PMC article.
-
A Plant-Derived Antioxidant Supplement Prevents the Loss of Retinal Ganglion Cells in the Retinas of NMDA-Injured Mice.Clin Ophthalmol. 2022 Mar 18;16:823-832. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S354958. eCollection 2022. Clin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35330750 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of Spermine Oxidase Suppresses Excitotoxicity Induced Neuroinflammation in Mouse Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 15;23(4):2133. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042133. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee A., Khurana I., Dhull C. (2019). Normal Tension Glaucoma versus Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma - the Autonomic Perspective. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 9 (6), 1–514. 10.5455/njppp.2019.9.0307323032019 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

