Towards Understanding the Usability Attributes of AI-Enabled eHealth Mobile Applications
- PMID: 34970424
- PMCID: PMC8714331
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5313027
Towards Understanding the Usability Attributes of AI-Enabled eHealth Mobile Applications
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Towards Understanding the Usability Attributes of AI-Enabled eHealth Mobile Applications.J Healthc Eng. 2023 May 24;2023:9896541. doi: 10.1155/2023/9896541. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37266199 Free PMC article.
Abstract
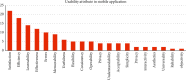
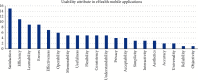
Mobile application (app) use is increasingly becoming an essential part of our daily lives. Due to their significant usefulness, people rely on them to perform multiple tasks seamlessly in almost all aspects of everyday life. Similarly, there has been immense progress in artificial intelligence (AI) technology, especially deep learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics. These technologies are now actively being implemented in smartphone apps and healthcare, providing multiple healthcare services. However, several factors affect the usefulness of mobile healthcare apps, and usability is an important one. There are various healthcare apps developed for each specific task, and the success of these apps depends on their performance. This study presents a systematic review of the existing apps and discusses their usability attributes. It highlights the usability models, outlines, and guidelines proposed in previous research for designing apps with improved usability characteristics. Thirty-nine research articles were reviewed and examined to identify the usability attributes, framework, and app design conducted. The results showed that satisfaction, efficiency, and learnability are the most important usability attributes to consider when designing eHealth mobile apps. Surprisingly, other significant attributes for healthcare apps, such as privacy and security, were not among the most indicated attributes in the studies.
Copyright © 2021 Adel Saeed Alzahrani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Alharbi A. I., Gay V., AlGhamdi M. J., Alturki R., Alyamani H. J. Towards an application helping to minimize medication error rate. Mobile Information Systems . 2021;2021:7. doi: 10.1155/2021/9221005.9221005 - DOI
-
- Komalavalli K., Hemalatha R., Dhanalakshmi S. A survey of artificial intelligence in smart phones and its applications among the students of higher education in and around Chennai city. Shanlax International Journal of Education . 2020;8(3):89–95. doi: 10.34293/education.v8i3.2379. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical