Different response to epidermal growth factor of hepatocytes in cultures isolated from male or female rat liver. Inhibitor effect of estrogen on binding and mitogenic effect of epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 3497071
- PMCID: PMC2962611
- DOI: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90924-3
Different response to epidermal growth factor of hepatocytes in cultures isolated from male or female rat liver. Inhibitor effect of estrogen on binding and mitogenic effect of epidermal growth factor
Abstract
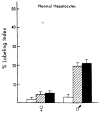
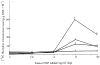
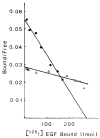
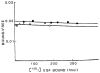
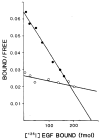
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis in hepatocytes isolated from the livers of male and female rats has been compared in monolayer culture. Plating efficiency, DNA and protein content, viability, and morphologic appearance were the same in cultures prepared with hepatocytes isolated from male or female rats. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced DNA synthesis was significantly higher in hepatocytes from male rats than in hepatocytes from female rats. This was the case whether hepatocytes were isolated from normal or partially hepatectomized male or female rats. Hepatocytes isolated from regenerating liver synthesize more DNA than those isolated from normal liver in response to EGF. This increased response to EGF in hepatocytes derived from regenerating liver was relatively the same for male- and female-derived hepatocytes, but the magnitude of the response was considerably higher in male-derived hepatocytes. In contrast, in vivo DNA synthesis in the liver remnant after partial hepatectomy was similar in male and female rats if measured 24 h after the operation. A comparison of EGF binding to male- and female-derived hepatocytes maintained in primary culture indicated a lower number of high-affinity receptors for EGF in the female hepatocytes. The addition of estrogen to primary cultures of hepatocytes isolated from male rats inhibited EGF binding as well as EGF-induced DNA synthesis. Our studies show significant differences in DNA synthesis in response to EGF when male and female hepatocytes are compared in primary culture. The regenerative response after partial hepatectomy, on the other hand, was the same in male and female rats. Thus, our studies indicate that the sex of the donor, rat is important when hepatocytes in culture are used for a variety of studies, such as hepatocyte metabolism, induction and control of DNA synthesis, and hepatocarcinogenesis. In addition, our results indicate that caution is advised when inferences are made from in vitro findings for in vivo conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor and proliferation in rat hepatocytes in primary culture isolated at different times after partial hepatectomy.Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1318-23. Cancer Res. 1986. PMID: 3002614 Free PMC article.
-
Self-regulating factor present in culture supernatants of regenerating hepatocytes in adult rats.J UOEH. 1990 Mar 1;12(1):1-17. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.12.1. J UOEH. 1990. PMID: 2110379
-
Effect of intracellular pH and two growth factors, epidermal growth factor and human hepatocyte growth factor, on DNA synthesis in non-regenerating and regenerating hepatocytes and hepatoma cells.Osaka City Med J. 1994 Dec;40(2):53-69. Osaka City Med J. 1994. PMID: 7862427
-
Differential proliferative response of cultured fetal and regenerating hepatocytes to growth factors and hormones.Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):495-500. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90104-g. Exp Cell Res. 1992. PMID: 1397101
-
Insulin-like growth factor-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptors are increased in hepatocytes from regenerating rat liver.Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2543-9. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2543. Endocrinology. 1990. PMID: 2158429
Cited by
-
Growth stimulation of primary rat hepatocytes by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Cell Biol Toxicol. 1993 Jan-Mar;9(1):15-31. doi: 10.1007/BF00755137. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1993. PMID: 8100183
-
Estrogens, androgens, and EGF receptor expression in gastric carcinoma induced by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine.Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Mar;39(3):635-40. doi: 10.1007/BF02088353. Dig Dis Sci. 1994. PMID: 8131702
-
Role of estrogens and epidermal growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Sep;36(9):1299-302. doi: 10.1007/BF01307526. Dig Dis Sci. 1991. PMID: 1654242 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of estrogen and tamoxifen on hepatocyte proliferation in vivo and in vitro.Hepatology. 1989 Apr;9(4):614-20. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090417. Hepatology. 1989. PMID: 2784403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koch KS, Leffert HL. Increased sodum ion influx is necessary to initiate rat hepatocyte proliferation. Cell. 1979;18:153–63. - PubMed
-
- Tomita V, Nakamura T, Ichihara A. Control of DNA synthesis and ornithine decarboxylase activity by hormones and amino acids in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1981;135:363–71. - PubMed
-
- Michalopoulos G, Cianciulli HD, Novotny AR, Kligerman AD, Strom SC, Jirtle RL. Liver regeneration studies with rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Cancer Res. 1982;42:4673–82. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa K, Watanabe K, Koga M. Induction of mitosis in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes under serum-free conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982;104:259–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

