Restricted survival benefit with right-censored data
- PMID: 34970772
- PMCID: PMC9162957
- DOI: 10.1002/bimj.202000392
Restricted survival benefit with right-censored data
Abstract
The hazard ratio is widely used to quantify treatment effects. However, it may be difficult to interpret for patients and practitioners, especially when the hazard ratio is not constant over time. Alternative measures of the treatment effects have been proposed such as the difference of the restricted mean survival times, the difference in survival proportions at some fixed follow-up time, or the net chance of a longer survival. In this paper, we propose the restricted survival benefit (RSB), a quantity that can incorporate multiple useful measurements of treatment effects. Hence, it provides a framework for a comprehensive assessment of the treatment effects. We provide estimation and inference procedures for the RSB that accommodate censored survival outcomes, using methods of the inverse-probability-censoring-weighted -statistic and the jackknife empirical likelihood. We conduct extensive simulation studies to examine the numerical performance of the proposed method, and we analyze data from a randomized Phase III clinical trial (SWOG S0777) using the proposed method.
Keywords: -statistic; inverse probability censoring weighting; jackknife empirical likelihood; restricted survival benefit.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
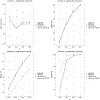
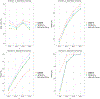
References
-
- Andersen PK and Gill RD (1982). Cox’s regression model for counting processes: a large sample study. Annals of Statistics, 10(4):1100–1120.
-
- Buyse M (2008). Letter to the editor: Reformulating the hazard ratio to enhance communication with clinical investigators. Clinical Trials, 5(6):641–642. - PubMed
-
- Datta S, Bandyopadhyay D, and Satten G (2010). Inverse probability of censoring weighted u-statistics for right-censored data with an application to testing hypotheses. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 37:680–700.
-
- Deville J and Särndal C-E (1992). Calibration estimators in survey sampling. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87(418):376–382.
-
- Durie BGM, Hoering A, Abidi MH, Rajkumar SV, Epstein J, Kahanic SP, Thakuri M, Reu F, Reynolds CM, Sexton R, Orlowski RZ, Barlogie B, and Dispenzieri A (2017). Bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma without intent for immediate autologous stem-cell transplant (swog s0777): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet, 389:519–527. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

