IgG1-b12-HIV-gp120 Interface in Solution: A Computational Study
- PMID: 34971312
- PMCID: PMC8790758
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c01143
IgG1-b12-HIV-gp120 Interface in Solution: A Computational Study
Abstract
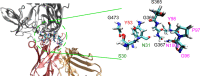
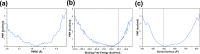
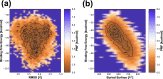
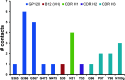
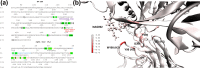
The use of broadly neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) has been shown to be a promising therapeutic modality in the prevention of HIV infection. Understanding the b12-gp120 binding mechanism under physiological conditions may assist the development of more broadly effective antibodies. In this work, the main conformations and interactions between the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of spike glycoprotein gp120 of HIV-1 and the IgG1-b12 mAb are studied. Accelerated molecular dynamics (aMD) and ab initio hybrid molecular dynamics have been combined to determine the most persistent interactions between the most populated conformations of the antibody-antigen complex under physiological conditions. The results show the most persistent receptor-binding mapping in the conformations of the antibody-antigen interface in solution. The binding-free-energy decomposition reveals a small enhancement in the contribution played by the CDR-H3 region to the b12-gp120 interface compared to the crystal structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


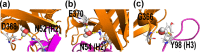
Similar articles
-
Molecular features of the broadly neutralizing immunoglobulin G1 b12 required for recognition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):5863-76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.5863-5876.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719580 Free PMC article.
-
A novel human antibody against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 is V1, V2, and V3 loop dependent and helps delimit the epitope of the broadly neutralizing antibody immunoglobulin G1 b12.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(12):6965-78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.12.6965-6978.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12768015 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Fab fragment of F105, a broadly reactive anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody that recognizes the CD4 binding site of HIV type 1 gp120.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(20):13060-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.13060-13069.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16189008 Free PMC article.
-
GP120: target for neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies.Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:739-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.24.021605.090557. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16551265 Review.
-
Structural Features of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies and Rational Design of Vaccine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1075:73-95. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0484-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030790 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational analysis of the IQSEC2 protein by statistical thermodynamics.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024 Oct 3;8:100158. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100158. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 39431217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallo R.; Salahuddin S.; Popovic M.; Shearer G.; Kaplan M.; Haynes B.; Palker T.; Redfield R.; Oleske J.; Safai B.; et al. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science 1984, 224, 500–503. 10.1126/science.6200936. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frank T. D.; Carter A.; Jahagirdar D.; Biehl M. H.; Douwes-Schultz D.; Larson S. L.; Arora M.; Dwyer-Lindgren L.; Steuben K. M.; Abbastabar H.; Abu-Raddad L. J.; Abyu D. M.; Adabi M.; Adebayo O. M.; Adekanmbi V.; Adetokunboh O. O.; Ahmadi A.; Ahmadi K.; Ahmadian E.; Ahmadpour E.; Ahmed M. B.; Akal C. G.; Alahdab F.; Alam N.; Albertson S. B.; Alemnew B. T. T.; Alene K. A.; Alipour V.; Alvis-Guzman N.; Amini S.; Anbari Z.; Anber N. H.; Anjomshoa M.; Antonio C. A. T.; Arabloo J.; Aremu O.; Areri H. A.; Asfaw E. T.; Ashagre A. F.; Asmelash D.; Asrat A. A.; Avokpaho E. F. G. A.; Awasthi A.; Awoke N.; Ayanore M. A.; Azari S.; Badawi A.; Bagherzadeh M.; Banach M.; Barac A.; Bärnighausen T. W.; Basu S.; Bedi N.; Behzadifar M.; Bekele B. B.; Belay S. A.; Belay Y. B.; Belayneh Y. M.; Berhane A.; Bhat A. G.; Bhattacharyya K.; Biadgo B.; Bijani A.; Bin Sayeed M. S.; Bitew H.; Blinov A.; Bogale K. A.; Bojia H. A.; Burugina Nagaraja S. B. N.; Butt Z. A.; Cahuana-Hurtado L.; Campuzano Rincon J. C.; Carvalho F.; Chattu V. K.; Christopher D. J.; Chu D.-T.; Crider R.; Dahiru T.; Dandona L.; Dandona R.; Daryani A.; das Neves J.; De Neve J.-W.; Degenhardt L.; Demeke F. M.; Demis A. B.; Demissie D. B.; Demoz G. T.; Deribe K.; Des Jarlais D.; Dhungana G. P.; Diaz D.; Djalalinia S.; Do H. P.; Doan L. P.; Duber H.; Dubey M.; Dubljanin E.; Duken E. E.; Duko Adema B.; Effiong A.; Eftekhari A.; El Sayed Zaki M.; El-Jaafary S. I.; El-Khatib Z.; Elsharkawy A.; Endries A. Y.; Eskandarieh S.; Eyawo O.; Farzadfar F.; Fatima B.; Fentahun N.; Fernandes E.; Filip I.; Fischer F.; Folayan M. O.; Foroutan M.; Fukumoto T.; Fullman N.; Garcia-Basteiro A. L.; Gayesa R. T.; Gebremedhin K. B.; Gebremeskel G. G. G.; Gebreyohannes K. K.; Gedefaw G. A.; Gelaw B. K.; Gesesew H. A.; Geta B.; Gezae K. E.; Ghadiri K.; Ghashghaee A.; Ginindza T. T. G.; Gugnani H. C.; Guimarães R. A.; Haile M. T.; Hailu G. B.; Haj-Mirzaian A.; Haj-Mirzaian A.; Hamidi S.; Handanagic S.; Handiso D. W.; Hanfore L. K.; Hasanzadeh A.; Hassankhani H.; Hassen H. Y.; Hay S. I.; Henok A.; Hoang C. L.; Hosgood H. D.; Hosseinzadeh M.; Hsairi M.; Ibitoye S. E.; Idrisov B.; Ikuta K. S.; Ilesanmi O. S.; Irvani S. S. N.; Iwu C. J.; Jacobsen K. H.; James S. L.; Jenabi E.; Jha R. P.; Jonas J. B.; Jorjoran Shushtari Z.; Kabir A.; Kabir Z.; Kadel R.; Kasaeian A.; Kassa B.; Kassa G. M.; Kassa T. D.; Kayode G. A.; Kebede M. M.; Kefale A. T.; Kengne A. P.; Khader Y. S.; Khafaie M. A.; Khalid N.; Khan E. A.; Khan G.; Khan J.; Khang Y.-H.; Khatab K.; Khazaei S.; Khoja A. T.; Kiadaliri A. A.; Kim Y. J.; Kisa A.; Kisa S.; Kochhar S.; Komaki H.; Koul P. A.; Koyanagi A.; Kuate Defo B.; Kumar G. A.; Kumar M.; Kuupiel D.; Lal D. K.; Lee J. J.-H.; Lenjebo T. L.; Leshargie C. T.; Macarayan E. R. K.; Maddison E. R.; Magdy Abd El Razek H.; Magis-Rodriguez C.; Mahasha P. W.; Majdan M.; Majeed A.; Malekzadeh R.; Manafi N.; Mapoma C. C.; Martins-Melo F. R.; Masaka A.; Mayenga E. N. L.; Mehta V.; Meles G. G.; Meles H. G.; Melese A.; Melku M.; Memiah P. T. N.; Memish Z. A.; Mena A. T.; Mendoza W.; Mengistu D. T.; Mengistu G.; Meretoja T. J.; Mestrovic T.; Miller T. R.; Moazen B.; Mohajer B.; Mohamadi-Bolbanabad A.; Mohammad K. A.; Mohammad Y.; Mohammad Darwesh A.; Mohammad Gholi Mezerji N.; Mohammadi M.; Mohammadibakhsh R.; Mohammadoo-Khorasani M.; Mohammed J. A.; Mohammed S.; Mohebi F.; Mokdad A. H.; Moodley Y.; Moossavi M.; Moradi G.; Moradi-Lakeh M.; Moschos M. M.; Mossie T. B.; Mousavi S. M.; Muchie K. F.; Muluneh A. G.; Muriithi M. K.; Mustafa G.; Muthupandian S.; Nagarajan A. J.; Naik G.; Najafi F.; Nazari J.; Ndwandwe D. E.; Nguyen C. T.; Nguyen H. L. T.; Nguyen S. H.; Nguyen T. H.; Ningrum D. N. A.; Nixon M. R.; Nnaji C. A.; Noroozi M.; Noubiap J. J.; Nourollahpour Shiadeh M.; Obsa M. S.; Odame E. A.; Ofori-Asenso R.; Ogbo F. A.; Okoro A.; Oladimeji O.; Olagunju A. T.; Olagunju T. O.; Olum S.; Oppong Asante K. O. A.; Oren E.; Otstavnov S. S.; Pa M.; Padubidri J. R.; Pakhale S.; Pakpour A. H.; Patel S. K.; Paulos K.; Pepito V. C. F.; Peprah E. K.; Piroozi B.; Pourshams A.; Qorbani M.; Rabiee M.; Rabiee N.; Radfar A.; Rafay A.; Rafiei A.; Rahim F.; Rahimi-Movaghar A.; Rahimi-Movaghar V.; Rahman S. U.; Ranabhat C. L.; Rawaf S.; Reis C.; Renjith V.; Reta M. A.; Rezai M. S.; Rios González C. M.; Roro E. M.; Rostami A.; Rubino S.; Saeedi Moghaddam S.; Safari S.; Sagar R.; Sahraian M. A.; Salem M. R. R.; Salimi Y.; Salomon J. A.; Sambala E. Z.; Samy A. M.; Sartorius B.; Satpathy M.; Sawhney M.; Sayyah M.; Schutte A. E.; Sepanlou S. G.; Seyedmousavi S.; Shabaninejad H.; Shaheen A. A.; Shaikh M. A.; Shallo S. A.; Shamsizadeh M.; Sharifi H.; Shibuya K.; Shin J. I.; Shirkoohi R.; Silva D. A. S.; Silveira D. G. A.; Singh J. A.; Sisay M. M. M.; Sisay M.; Sisay S.; Smith A. E.; Sokhan A.; Somayaji R.; Soshnikov S.; Stein D. J.; Sufiyan M. B.; Sunguya B. F.; Sykes B. L.; Tadesse B. T.; Tadesse D. B.; Tamirat K. S.; Taveira N.; Tekelemedhin S. W.; Temesgen H. D.; Tesfay F. H.; Teshale M. Y.; Thapa S.; Tlaye K. G.; Topp S. M.; Tovani-Palone M. R.; Tran B. X.; Tran K. B.; Ullah I.; Unnikrishnan B.; Uthman O. A.; Veisani Y.; Vladimirov S. K.; Wada F. W.; Waheed Y.; Weldegwergs K. G.; Weldesamuel G. T. T.; Westerman R.; Wijeratne T.; Wolde H. F.; Wondafrash D. Z.; Wonde T. E.; Wondmagegn B. Y.; Yeshanew A. G.; Yilma M. T.; Yimer E. M.; Yonemoto N.; Yotebieng M.; Youm Y.; Yu C.; Zaidi Z.; Zarghi A.; Zenebe Z. M.; Zewale T. A.; Ziapour A.; Zodpey S.; Naghavi M.; Vollset S. E.; Wang H.; Lim S. S.; Kyu H. H.; Murray C. J. L. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and mortality of HIV, 1980–2017, and forecasts to 2030, for 195 countries and territories: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017. Lancet HIV 2019, 6, e831–e859. 10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30196-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

