CN470 is a BET/CBP/p300 multi-bromodomain inhibitor and has an anti-tumor activity against MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 34971957
- PMCID: PMC8898544
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.12.078
CN470 is a BET/CBP/p300 multi-bromodomain inhibitor and has an anti-tumor activity against MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
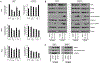
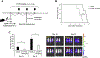
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with chromosomal rearrangements involving the mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) gene (MLL-r ALL) remains an incurable disease. Thus, development of a safe and effective therapeutic agent to treat this disease is crucial to address this unmet medical need. BRD4, a member of the bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) protein family, and cyclic AMP response element binding protein binding protein (CBP) and p300, two paralogous histone acetyltransferases, are all considered cancer drug targets and simultaneous targeting of these proteins may have therapeutic advantages. Here, we demonstrate that a BET/CBP/p300 multi-bromodomain inhibitor, CN470, has anti-tumor activity against MLL-r ALL in vitro and in vivo. CN470, potently inhibited ligand binding to the bromodomains of BRD4, CBP, and p300 and suppressed the growth of MLL-r ALL cell lines and patient-derived cells with MLL rearrangements. CN470 suppressed mRNA and protein expression of MYC and induced apoptosis in MLL-r ALL cells, following a cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. Moreover, CN470 reduced BRD4 binding to acetylated histone H3. The in vivo effects of CN470 were investigated using SEMLuc/GFP cells expressing luminescent markers in an orthotopic mouse model. Mice administered CN470 daily had prolonged survival compared to the vehicle group. Further, CN470 also showed anti-tumor effects against an MLL-r ALL patient-derived xenograft model. These findings suggest that inhibition of BET/CBP/p300 by the multi-bromodomain inhibitor, CN470, represents a promising therapeutic approach against MLL-r ALL.
Keywords: ALL; BET; Bromodomain; CBP/p300; MLL; PDX.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest N. Imayoshi, K. Tanaka, S.-M. Yang, K. Akahane, Y. Toda, S. Hosogi, T. Inukai, S, Okada, D. J. Maloney, I. Kato and E. Ashihara have no financial conflict of interest to disclose. M. Yoshioka is an employee of ConverGene LLC and holds equity in the company.
Figures
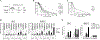
Similar articles
-
The CDK4/6-UCHL5-BRD4 axis confers resistance to BET inhibitors in MLL-rearranged leukemia cells by suppressing BRD4 protein degradation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Jan 15;588:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.12.063. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 34954522
-
Combined Targeting of the BRD4-NUT-p300 Axis in NUT Midline Carcinoma by Dual Selective Bromodomain Inhibitor, NEO2734.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Jul;19(7):1406-1414. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0087. Epub 2020 May 5. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32371576 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity of inhibitors tackling the differentiation blockage of MLL-rearranged leukemia.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Jun 28;12(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0749-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31253180 Free PMC article.
-
MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Apr;15(2):83-89. doi: 10.1007/s11899-020-00582-5. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020. PMID: 32350732 Review.
-
Leukemogenesis via aberrant self-renewal by the MLL/AEP-mediated transcriptional activation system.Cancer Sci. 2021 Oct;112(10):3935-3944. doi: 10.1111/cas.15054. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 34251718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of the p300/CBP histone acetyltransferases in human cancer.Epigenomics. 2025 Feb;17(3):193-208. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2024.2447807. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 39929233 Review.
-
Depletion of DNTTIP2 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024 Jan-Feb;21(1):18-29. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20426. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38151292 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of CREBBP/EP300 and Its Therapeutic Implications in Hematological Malignancies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;15(4):1219. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041219. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic targeting in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with aberrant HOX/MEIS1 expression.Eur J Med Genet. 2023 Dec;66(12):104869. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2023.104869. Epub 2023 Oct 29. Eur J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 38174649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The important role of the histone acetyltransferases p300/CBP in cancer and the promising anticancer effects of p300/CBP inhibitors.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Jan 17;41(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09984-0. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39825161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong GT, Kawashima T, Leisenring W, Stratton K, Stovall M, Hudson MM, Sklar CA, Robison LL, Oeffinger KC, Aging and risk of severe, disabling, life-threatening, and fatal events in the childhood cancer survivor study, J. Clin. Oncol. 32 (2014) 1218–1227. 10.1200/JCO.2013.51.1055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berthon C, Raffoux E, Thomas X, Vey N, Gomez-Roca C, Yee K, Taussig DC, Rezai K, Roumier C, Herait P, Kahatt C, Quesnel B, Michallet M, Recher C, Lokiec F, Preudhomme C, Dombret H, Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with acute leukaemia: A dose-escalation, phase 1 study, Lancet Haematol. 3 (2016) e186–e195. 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00247-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittmann A, Giotopoulos G, Bantscheff M, Chan WI, Robson SC, Chung CW, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Huthmacher C, Gudgin E, Lugo D, Beinke S, Chapman TD, Roberts EJ, Soden PE, Auger KR, Mirguet O, Doehner K, Delwel R, Burnett AK, Jeffrey P, Drewes G, Lee K, Huntly BJP, Kouzarides T, Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia, Nature. 478 (2011) 529–533. 10.1038/nature10509. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piha-Paul SA, Hann CL, French CA, Cousin S, Braña I, Cassier PA, Moreno V, de Bono JS, Harward SD, Ferron-Brady G, Barbash O, Wyce A, Wu Y, Horner T, Annan M, Parr NJ, Prinjha RK, Carpenter CL, Hilton J, Hong DS, Haas NB, Markowski MC, Dhar A, O’Dwyer PJ, Shapiro GI, Phase 1 study of molibresib (GSK525762), a bromodomain and extra-terminal domain protein inhibitor, in NUT carcinoma and other solid tumors, JNCI Cancer Spectr. 4 (2020) 1–9. 10.1093/JNCICS/PKZ093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piha-Paul SA, Sachdev JC, Barve M, LoRusso P, Szmulewitz R, Patel SP, Lara PN, Chen X, Hu B, Freise KJ, Modi D, Sood A, Hutti JE, Wolff J, O’Neil BH, First-in-human study of mivebresib (ABBV-075), an oral pan-inhibitor of bromodomain and extra terminal proteins, in patients with relapsed/ refractory solid tumors, Clin. Cancer Res. 25 (2019) 6309–6319. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0578. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

