A computer-aided diagnosis system for the classification of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 pneumonia on chest X-ray images by integrating CNN with sparse autoencoder and feed forward neural network
- PMID: 34971978
- PMCID: PMC8668604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105134
A computer-aided diagnosis system for the classification of COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 pneumonia on chest X-ray images by integrating CNN with sparse autoencoder and feed forward neural network
Abstract
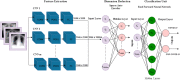
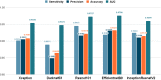
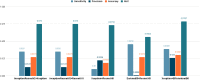
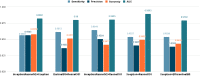
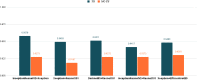
Several infectious diseases have affected the lives of many people and have caused great dilemmas all over the world. COVID-19 was declared a pandemic caused by a newly discovered virus named Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by the World Health Organisation in 2019. RT-PCR is considered the golden standard for COVID-19 detection. Due to the limited RT-PCR resources, early diagnosis of the disease has become a challenge. Radiographic images such as Ultrasound, CT scans, X-rays can be used for the detection of the deathly disease. Developing deep learning models using radiographic images for detecting COVID-19 can assist in countering the outbreak of the virus. This paper presents a computer-aided detection model utilizing chest X-ray images for combating the pandemic. Several pre-trained networks and their combinations have been used for developing the model. The method uses features extracted from pre-trained networks along with Sparse autoencoder for dimensionality reduction and a Feed Forward Neural Network (FFNN) for the detection of COVID-19. Two publicly available chest X-ray image datasets, consisting of 504 COVID-19 images and 542 non-COVID-19 images, have been combined to train the model. The method was able to achieve an accuracy of 0.9578 and an AUC of 0.9821, using the combination of InceptionResnetV2 and Xception. Experiments have proved that the accuracy of the model improves with the usage of sparse autoencoder as the dimensionality reduction technique.
Keywords: CNN; COVID-19; Computer-aided detection; Feed forward neural network; Sparse autoencoder.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- MAP COVID . BBC News. Disponível em; 2021. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-51235105 (Coronavirus Cases, Deaths, Vaccinations by Country).
-
- Zemouri Ryad, Zerhouni Noureddine, Racoceanu Daniel. Deep learning in the biomedical applications: recent and future status. Appl. Sci. 2019;9(8):1526.
-
- Dudhane A., Shingadkar G., Sanghavi P., Jankharia B., Talbar S. Interstitial lung disease classification using feed forward neural networks. Adv. Intell. Syst. Res. ICCASP. 2017;137:515–521.
-
- Acharya U Rajendra, Oh Shu Lih, Hagiwara Yuki, Tan Jen Hong, Adeli Hojjat, Subha D Puthankattil. Automated eeg-based screening of depression using deep convolutional neural network. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2018;161:103–113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

