Emerging rejuvenation strategies-Reducing the biological age
- PMID: 34972247
- PMCID: PMC8761015
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13538
Emerging rejuvenation strategies-Reducing the biological age
Abstract
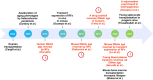
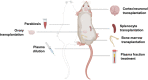
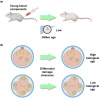
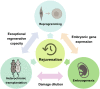
Several interventions have recently emerged that were proposed to reverse rather than just attenuate aging, but the criteria for what it takes to achieve rejuvenation remain controversial. Distinguishing potential rejuvenation therapies from other longevity interventions, such as those that slow down aging, is challenging, and these anti-aging strategies are often referred to interchangeably. We suggest that the prerequisite for a rejuvenation intervention is a robust, sustained, and systemic reduction in biological age, which can be assessed by biomarkers of aging, such as epigenetic clocks. We discuss known and putative rejuvenation interventions and comparatively analyze them to explore underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: aging; biomarkers; epigenetic clocks; rejuvenation.
© 2021 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abad, M. , Mosteiro, L. , Pantoja, C. , Cañamero, M. , Rayon, T. , Ors, I. , Graña, O. , Megías, D. , Domínguez, O. , Martínez, D. , Manzanares, M. , Ortega, S. , & Serrano, M. (2013). Reprogramming in vivo produces teratomas and iPS cells with totipotency features. Nature, 502(7471), 340–345. 10.1038/nature12586 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baar, M. P. , Brandt, R. M. C. , Putavet, D. A. , Klein, J. D. D. , Derks, K. W. J. , Bourgeois, B. R. M. , Stryeck, S. , Rijksen, Y. , van Willigenburg, H. , Feijtel, D. A. , van der Pluijm, I. , Essers, J. , van Cappellen, W. A. , van IJcken, W. F. , Houtsmuller, A. B. , Pothof, J. , de Bruin, R. W. F. , Madl, T. , Hoeijmakers, J. H. J. , … de Keizer, P. L. J. (2017). Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging. Cell, 169(1), 132–147 e116. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.031 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, D. J. , Childs, B. G. , Durik, M. , Wijers, M. E. , Sieben, C. J. , Zhong, J. , A. Saltness, R. , Jeganathan, K. B. , Verzosa, G. C. , Pezeshki, A. , Khazaie, K. , Miller, J. D. , & van Deursen, J. M. (2016). Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)‐positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature, 530(7589), 184–189. 10.1038/nature16932 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

