Cost-Effectiveness of perioperative Vaginally Administered estrogen in postmenopausal women undergoing prolapse surgery (EVA trial): study protocol for a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 34972504
- PMCID: PMC8720212
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-021-01587-9
Cost-Effectiveness of perioperative Vaginally Administered estrogen in postmenopausal women undergoing prolapse surgery (EVA trial): study protocol for a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Surgery for pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is associated with high recurrence rates. The costs associated with the treatment of recurrent POP are huge, and the burden from women who encounter recurrent POP, negatively impacts their quality of life. Estrogen therapy might improve surgical outcome for POP due to its potential beneficial effects. It is thought that vaginal estrogen therapy improves healing and long-term maintenance of connective tissue integrity. Hence, this study aims to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of perioperative vaginal estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women undergoing POP surgery.
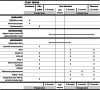
Methods: The EVA trial is a multi-center double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial conducted in the Netherlands comparing the effectiveness and costs-effectiveness of vaginal estrogen therapy. This will be studied in 300 postmenopausal women undergoing primary POP surgery, with a POP-Q stage of ≥ 2. After randomization, participants administer vaginal estrogen cream or placebo cream from 4 to 6 weeks preoperative until 12 months postoperative. The primary outcome is subjective improvement of POP symptoms at 1 year follow-up, measured with the Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI-I) scale. Secondary outcomes are POP-Q anatomy in all compartments, re-interventions, surgery related complications, general and disease specific quality of life, sexual function, signs and complaints of vaginal atrophy, vaginal pH, adverse events, costs, and adherence to treatment. Follow up is scheduled at 6 weeks, 6 months and 12 months postoperative. Data will be collected using validated questionnaires and out-patient visits including gynecological examination performed by an independent gynecologist.
Discussion: This study investigates whether perioperative vaginal estrogen will be cost-effective in the surgical treatment of POP in postmenopausal women. It is hypothesized that estrogen therapy will show a reduction in recurrent POP symptoms and a reduction in reoperations for POP, with subsequent improved quality of life among women and cost savings. Trial registrationNetherlands Trial Registry: NL6853; registered 19-02-2018, https://www.trialregister.nl/trial/6853 . EudraCT: 2017-003144-21; registered: 24-07-2017.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness; Pelvic organ prolapse; Pelvic reconstructive surgery; Postmenopausal; Recurrence; Vaginal estrogen therapy; Wound healing.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Slieker-ten Hove MC, Pool-Goudzwaard AL, Eijkemans MJ, Steegers-Theunissen RP, Burger CW, Vierhout ME. The prevalence of pelvic organ prolapse symptoms and signs and their relation with bladder and bowel disorders in a general female population. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009;20(9):1037–1045. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hendrix SL, Clark A, Nygaard I, Aragaki A, Barnabei V, McTiernan A. Pelvic organ prolapse in the Women's Health Initiative: gravity and gravidity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186(6):1160–1166. - PubMed
-
- Swift S, Woodman P, O'Boyle A, Kahn M, Valley M, Bland D, et al. Pelvic Organ Support Study (POSST): the distribution, clinical definition, and epidemiologic condition of pelvic organ support defects. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192(3):795–806. - PubMed
-
- Swift SE. The distribution of pelvic organ support in a population of female subjects seen for routine gynecologic health care. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183(2):277–285. - PubMed
-
- Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology, American Urogynecologic Society Practice bulletin no. 185: pelvic organ prolapse. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(5):e234–e250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

