Proton pump inhibitors associated with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder
- PMID: 34972777
- PMCID: PMC8720946
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-246469
Proton pump inhibitors associated with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder
Abstract
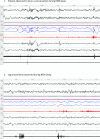
We present the case of a 65-year-old woman diagnosed with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder (REMBD) based on typical symptoms and confirmed with an inpatient polysomnogram. She was prescribed clonazepam and later temazepam but continued to have intrusive symptoms. She subsequently recalled that the onset of dream enactment coincided with starting high-dose omeprazole for acid reflux. With this insight, she stopped the omeprazole. Within days, the dream enactment and nocturnal movements subsided. She stopped taking the temazepam and was symptom free for a few months. However, she was started on lansoprazole for recurrent dyspepsia. Once again she experienced violent movements in sleep. This is the first time an association between proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and REMBD has been reported. PPIs have many effects on the central nervous system and should be considered as a possible provoking factor in people presenting with REMBD.
Keywords: sleep disorders (respiratory medicine); unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bassetti CL, Dogas Z, Peigneux P. Physiological basis of sleep, sleep medicine textbook, European sleep research Society, 2014: 1–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical