Sex- and Age-Specific Centile Curves and Downloadable Calculator for Clinical Muscle Strength Tests to Identify Probable Sarcopenia
- PMID: 34972866
- PMCID: PMC9005054
- DOI: 10.1093/ptj/pzab299
Sex- and Age-Specific Centile Curves and Downloadable Calculator for Clinical Muscle Strength Tests to Identify Probable Sarcopenia
Abstract
Objective: Identifying muscle weakness and probable sarcopenia using strength tests requires reference data. This study aimed to provide age- and sex-specific normative data for grip strength and common variations of the Sit-to-Stand (STS) test: time to complete 5 stands (5x-STS) and number of stands completed in 30 seconds (30s-STS). Predictors of test performance were also explored.
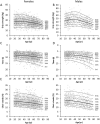
Methods: Dominant hand grip strength was assessed in adults (age = 18-80 years) using a digital dynamometer, and 5x-STS and 30s-STS performance were assessed synchronously during a single 30-second test. Sex-specific centile curves were generated using the lambda-mu-sigma method.
Results: Data from 2301 participants (female = 1682, male = 619) were included. Peak median grip strength occurred in female participants at 33.9 years of age (27.9 kg) and in male participants at 37.6 years of age (47.2 kg). 5x-STS and 30s-STS performance peaked at the youngest age (18.0 years) in both female participants (8.16 seconds and 17.2 repetitions) and male participants (8.02 seconds and 17.7 repetitions). Test performances were lowest for all tests at the oldest age in the database. Predictors of better test performance included lower age and higher self-reported physical functioning and appendicular skeletal muscle mass, to name a few. White participants had better performance than Black participants on the STS tests.
Conclusion: The generated centile curves reveal the pattern of change in muscle strength for tests recommended to identify probable sarcopenia. The curves can be used in rehabilitation to assess an individual's performance relative to sex- and age-specific norms. To aid use of the data, a downloadable Excel-based calculator is provided to compute participant-specific percentiles, z scores, and t scores for each outcome and plot performance on the centile curves.
Impact: Physical therapists have an important role in identifying and treating individuals with sarcopenia and other causes of muscle weakness. The reference data provided for common clinical muscle strength tests provide therapists an ability to assess an individual's relative performance.
Lay summary: Knowing the normal or expected strength for an individual's age and sex is essential to identifying muscle weakness. This study provides age- and sex-specific normal values for hand grip strength and sit-to-stand tests in adults aged 18 to 80 years.
Keywords: Cachexia; Chair Stand Test; Grip Strength; Normative Data; Sarcopenia; Sit To Stand Test.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Physical Therapy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance on sit-to-stand tests in relation to measures of functional fitness and sarcopenia diagnosis in community-dwelling older adults.Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021 Jan 8;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s11556-020-00255-5. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2021. PMID: 33419399 Free PMC article.
-
Normative values of muscle strength across ages in a 'real world' population: results from the longevity check-up 7+ project.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020 Dec;11(6):1562-1569. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12610. Epub 2020 Nov 4. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020. PMID: 33147374 Free PMC article.
-
Physical working capacity at fatigue threshold (PWCFT) is associated with sarcopenia-related body composition and measures of functionality in older adults.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014 Sep-Oct;59(2):300-4. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2014.04.012. Epub 2014 May 4. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014. PMID: 24856645
-
Cut-off points for knee extension strength: identifying muscle weakness in older adults.Eur Geriatr Med. 2024 Aug;15(4):913-925. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-01009-7. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Eur Geriatr Med. 2024. PMID: 38926333 Review.
-
Comprehensive Assessment of Lower Limb Function and Muscle Strength in Sarcopenia: Insights from the Sit-to-Stand Test.Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2024 Mar;28(1):1-8. doi: 10.4235/agmr.23.0205. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Ann Geriatr Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38325818 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fracture discrimination capability of ulnar flexural rigidity measured via Cortical Bone Mechanics Technology: study protocol for The STRONGER Study.JBMR Plus. 2024 Jan 4;8(1):ziad002. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziad002. eCollection 2024 Jan. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 38690126 Free PMC article.
-
Hand grip strength should be normalized by weight not height for eliminating the influence of individual differences: Findings from a cross-sectional study of 1,511 healthy undergraduates.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 18;9:1063939. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1063939. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36741997 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid formation is driven by crosstalk between skeletal muscle and other cell types.JCI Insight. 2024 Jan 23;9(2):e171815. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.171815. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38032735 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between klotho and physical function in healthy aging.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 30;13(1):21158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47791-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38036596 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of milk fat globule membrane ingestion with exercise on physical strength in healthy young adults: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2535372. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2535372. Epub 2025 Jul 20. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40684312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393:2636–2646. - PubMed
-
- Beaudart C, Rolland Y, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, et al. Assessment of muscle function and physical performance in daily clinical practice: a position paper endorsed by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal diseases (ESCEO). Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;105:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Chen L-K, Woo J, Assantachai P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21:300–307.e2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

