A 52-Year-Old Man with a Gustillo-Anderson IIIB Open Tibial Shaft Fracture with Extensive Soft-Tissue Defect Requiring Limb Salvage with Artificial Deformity-Creating Technique
- PMID: 34974514
- PMCID: PMC8740537
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.934788
A 52-Year-Old Man with a Gustillo-Anderson IIIB Open Tibial Shaft Fracture with Extensive Soft-Tissue Defect Requiring Limb Salvage with Artificial Deformity-Creating Technique
Abstract
BACKGROUND In this case report, an alternative way of treating Gustillo-Anderson IIIB type fractures with severe soft-tissue damage is provided for cases where, for various reasons, it is not possible to close a soft-tissue defect with a flap. CASE REPORT An artificial deformity-creating technique was applied for a patient with a right distal tibial open fracture (Gustillo IIIB type) with complete tibial cartilage and bone loss of 10 cm and severe soft-tissue defect after high-energy trauma. This technique includes damaged limb shortening, translation, angulation, and rotation for closure of soft-tissue defects using orthopedic hexapod and bifocal bone transport without need for plastic surgery. Because of the timely planning and application of the orthopedic hexapod for the artificial deformity correction, the final alignment of the limb was close to the physiological standard and had good functional outcomes. Despite the extremely severe shortening and acute angles, the total treatment time was only 75 weeks. At the 1-year follow-up after treatment completion, the patient had good functional outcomes with the 36-Item Short Form Survey score: general health, 80%; physical functioning, 85%; and social functioning, 100%. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, we show that the artificial deformity-creating with subsequent orthopedic hexapod application and lengthening of a limb is a robust method that can be applied even for the treatment of severe open fractures with significant soft-tissue damage and bone loss, which can be performed outside high-level trauma hospitals and has good clinical outcomes without significant complications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


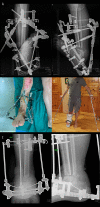
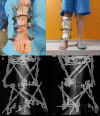
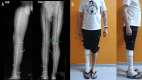
References
-
- Gopal S, Majumder S, Batchelor AG, et al. Fix and flap̺ The radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(7):959–66. - PubMed
-
- Poletti FL, Macmull S, Mushtaq N, Mobasheri R. Current concepts and principles in open tibial fractures – part II management. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol. 2017;8(2):00305.
-
- Hsu JR, Beltran MJ, Skeletal Trauma Research Consortium Shortening and angulation for soft-tissue reconstruction of extremity wounds in a combat support hospital. Mil Med. 2009;174(8):838–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

