The protective effects of dezocine on interleukin-1β-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and the possible mechanisms
- PMID: 34974796
- PMCID: PMC8805889
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2017700
The protective effects of dezocine on interleukin-1β-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and the possible mechanisms
Abstract
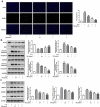
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a natural problem linked to the inflammation. We aimed to investigate the role of dezocine (DEZ) in the development of IDD. Human nucleus pulposus cells (HNPCs) induced by interleukin (IL)-1β was used as a cellular model of IDD. After treatment with DEZ, HNPCs viability was evaluated with a CCK-8 assay. Then, the levels of inflammatory factors, including IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and oxidative stress-related markers, including reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA) and reduced glutathione (GSH), were tested by RT-qPCR or kits. TUNEL staining was employed to detect cell apoptosis and Western blot was used to determine the expression of proteins related to inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and MAPK signaling. Afterward, PMA, a MAPK signaling pathway agonist, was adopted for exploring the regulatory effects of DEZ on MAPK pathway. Results indicated that DEZ enhanced cell viability of HNPCs after IL-1β exposure. DEZ alleviated the inflammation and oxidative stress, evidenced by decreased levels of IL-6, TNF-α, ROS, MDA, p-NF-κB p65, NF-κB p65 in nucleus, cox-2 and increased levels of NF-κB p65 in cytoplasm, GSH, SOD1 and SOD2. Moreover, DEZ notably inhibited IL-1β-induced apoptosis of HNPCs. Furthermore, DEZ suppressed the levels of ERS-related proteins. The levels of related proteins in MAPK signaling including p-P38 and p-ERK1/2 were remarkably reduced after DEZ administration. By contrast, PMA crippled the impacts of DEZ on inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis of HNPCs induced by IL-1β. Collectively, DEZ ameliorates IL-1β-induced HNPCs injury via inhibiting MAPK signaling.
Keywords: Intervertebral disc degeneration; dezocine; endoplasmic reticulum stress; human nucleus pulposus cells; inflammation; mapk.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
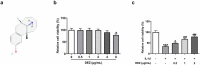




Similar articles
-
ZNF667 alleviates the inflammatory damage in intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 28;49(10):1611-1621. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240122. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40074310 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Emodin protects against apoptosis and inflammation by regulating reactive oxygen species-mediated NF-κB signaling in interleukin-1β-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023 Jan-Dec;42:9603271221138552. doi: 10.1177/09603271221138552. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36598795
-
Baicalin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix degradation in human nucleus pulposus cells.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023 Dec;45(4):433-442. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2023.2165942. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023. PMID: 36617937
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress associates with the development of intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 12;13:1094394. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1094394. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36714579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Signaling Pathway, and Therapy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 10;2022:1984742. doi: 10.1155/2022/1984742. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36262281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tetrandrine reduces oxidative stress, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation and improves intervertebral disc degeneration by inducing autophagy.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):3944-3957. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2031396. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35109761 Free PMC article.
-
Omentin-1 alleviate interleukin-1β(IL-1β)-induced nucleus pulposus cells senescence.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13849-13859. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2084495. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35707832 Free PMC article.
-
Three Classes of Antioxidant Defense Systems and the Development of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 3;13:840293. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.840293. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35309045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis by downregulating the NF-κB pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):4455-4467. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2033403. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35152855 Free PMC article.
-
Sinomenine Ameliorates IL-1β-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Rats Through Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Oct 20;16:4777-4791. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S430423. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37881650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fontana G, See E, Pandit A. Current trends in biologics delivery to restore intervertebral disc anabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84:146–158. - PubMed
-
- Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(4):487–492. - PubMed
-
- Manek NJ, MacGregor AJ. Epidemiology of back disorders: prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17(2):134–140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
