Human bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-188 reduces bronchial smooth muscle cell proliferation in asthma through suppressing the JARID2/Wnt/β-catenin axis
- PMID: 34974799
- PMCID: PMC8855860
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2021.2020432
Human bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-188 reduces bronchial smooth muscle cell proliferation in asthma through suppressing the JARID2/Wnt/β-catenin axis
Abstract
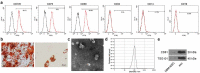
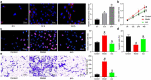
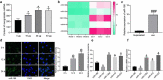
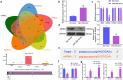
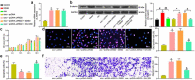
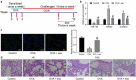
The functions of exosomes in allergic diseases including asthma have aroused increasing concerns. This paper focuses on the effects of exosomes derived from human bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells (hBM-MSCs) on the proliferation of bronchial smooth muscle cells in asthma and the mechanism involved. Exosomes were extracted from hBM-MSCs and identified. Human BSMCs were induced with transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 to mimic an asthma-like condition in vitro and then treated with exosomes. A mouse model with asthma was induced by ovalbumin (OVA) and treated with exosomes for in vivo study. The hBM-MSC-derived exosomes significantly reduced the abnormal proliferation and migration of TGF-β1-treated BSMCs. microRNA (miR)-188 was the most enriched miRNA in exosomes according the microarray analysis, and JARID2 was identified as a mRNA target of miR-188. Either downregulation of miR-188 or upregulation of JARID2 blocked the protective effects of exosomes on BSMCs. JARID2 activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In the asthmatic mice, hBM-MSC-derived exosomes reduced inflammatory cell infiltration, mucus production, and collagen deposition in mouse lung tissues. In conclusion, this study suggestes that hBM-MSC-derived exosomes suppress proliferation of BSMCs and lung injury in asthmatic mice through the miR-188/JARID2/Wnt/β-catenin axis. This study may provide novel insights into asthma management.
Keywords: Human bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells; JARID2; asthma; bronchial smooth muscle cells; exosomes; microRNA-188; wnt/β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-133b suppresses glioma progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting EZH2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Dec 16;10(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1446-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31842978 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-141 targets PTEN and activates β-catenin to alleviate myocardial injury in septic mice.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021 Oct;43(5):584-593. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1955920. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34308733
-
MSCs reduce airway remodeling in the lungs of asthmatic rats through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Nov;24(21):11199-11211. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202011_23608. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33215438
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their MicroRNAs in Heart Repair and Regeneration.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Jun;17(3):505-522. doi: 10.1007/s12265-023-10449-8. Epub 2023 Oct 24. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37875715 Review.
-
Mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes in the treatment of age-related diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 May 18;14:1181308. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181308. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37275920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Scutellarin Alleviates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway Remodeling in Mice and TGF-β-Induced Pro-fibrotic Phenotype in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells via MAPK and Smad2/3 Signaling Pathways.Inflammation. 2024 Jun;47(3):853-873. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01947-7. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38168709 Free PMC article.
-
Potential angiogenic, immunomodulatory, and antifibrotic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in systemic sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2023 May 12;14:1125257. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125257. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37251412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M2 macrophage-derived exosomes reverse TGF-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transformation in BEAS-2B cells via the TGF-βRI/Smad2/3 signaling pathway.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 11;30(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02516-4. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40211426 Free PMC article.
-
Nebulization of Hypoxic hUCMSC-EVs Attenuates Airway Epithelial Barrier Defects in Chronic Asthma Mice by Transferring CAV-1.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 29;19:10941-10959. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S476151. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39493276 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of hypoxia on the expression of microRNA in extracellular vesicles of human umbilical cord stem cells in vitro.Cell Tissue Bank. 2023 Dec;24(4):769-778. doi: 10.1007/s10561-023-10095-z. Epub 2023 May 24. Cell Tissue Bank. 2023. PMID: 37221283
References
-
- Nanda A, Wasan AN.. Asthma in adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Schatz M, Rosenwasser L. The allergic asthma phenotype. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2014;2:645–648. quiz 9. - PubMed
-
- Boonpiyathad T, Sozener ZC, Satitsuksanoa P, et al. Immunologic mechanisms in asthma. Semin Immunol. 2019;46:101333. - PubMed
-
- Wang YC, Jaakkola MS, Lajunen TK, et al. Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome among subjects with newly diagnosed adult-onset asthma. Allergy. 2018;73:1554–1557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
