Preparation and characterization of scutellarin loaded on ultradeformable nano-liposomes scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) and in vitro study of its osteogenesis
- PMID: 34974800
- PMCID: PMC8805926
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2016095
Preparation and characterization of scutellarin loaded on ultradeformable nano-liposomes scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) and in vitro study of its osteogenesis
Abstract
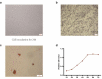
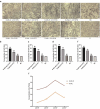
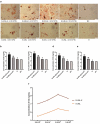
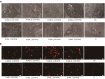
The present research aimed to elucidate a convenient, safe and economic approach to induce the growth of endogenous bone tissue and bone regeneration. S-UNL-E was prepared using reverse-phase evaporation, and scutellarin encapsulation was subsequently compared. Meanwhile, the optimal preparation scheme was developed using an orthogonal method, and the particle size was determined using laser light scattering. In osteoblasts cultured in vitro, methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining and alizarin red staining were used to detect the osteogenic effects of S-UNL-E. The results indicated that the optimal process conditions for S-UNL-E included mass ratios of phospholipid-cholesterol, phospholipid-breviscapine, phospholipid-sodium cholate, and phospholipid-stearamide were 2:1, 15:1, 7:1 and 7:1, respectively, and the mass of ethylenediamine tetramethylphosphonic acid (EDTMP) was 30 mg. The average particle size of S-UNL-E was 156.67 ± 1.76 nm, and Zeta potential was -28.77 ± 0.66 mv. S-UNL-E substantially increased the expression of ALP osteoblasts, elevated the content of osteocalcin protein and promoted the formation of mineralized nodules. Cells in the S-UNL-E group were densely distributed with integrated cell structure, and the actin filaments were clear and obvious. The findings demonstrated that S-UNL-E greatly promoted the differentiation and maturation of osteoblasts, and S-UNL-E (2.5 × 108) produced the most favorable effect in differentiation promotion. In conclusion, the present study successfully constructed an S-UNL-E material characterized by high encapsulation and high stability, which could effectively promote osteogenic differentiation and bone formation.
Keywords: S-UNL-E; encapsulation; osteogenic differentiation; scutellarin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Scutellarin Loaded on Ultradeformable Nanoliposome Scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) Promotes Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Aug 16;2022:1395299. doi: 10.1155/2022/1395299. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. Retraction in: Stem Cells Int. 2023 Dec 20;2023:9851693. doi: 10.1155/2023/9851693. PMID: 36017130 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Scutellarin enhances osteoblast proliferation and function via NF-κB-mediated CXCR4 induction.Gene. 2018 Nov 15;676:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.068. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29936266
-
Osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: melatonin as a differentiation factor.Iran Biomed J. 2008 Jul;12(3):133-41. Iran Biomed J. 2008. PMID: 18762816
-
Berberine Promotes the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Alveolar Osteoblasts through Regulating the Expression of miR-214.Pharmacology. 2021;106(1-2):70-78. doi: 10.1159/000508972. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Pharmacology. 2021. PMID: 32688361
-
Sulfuretin promotes osteoblastic differentiation in primary cultured osteoblasts and in vivo bone healing.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):78320-78330. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12460. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713171 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of scutellarin on the mechanism of cardiovascular diseases: a review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1329969. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1329969. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38259289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scutellarin Loaded on Ultradeformable Nanoliposome Scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) Promotes Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Aug 16;2022:1395299. doi: 10.1155/2022/1395299. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. Retraction in: Stem Cells Int. 2023 Dec 20;2023:9851693. doi: 10.1155/2023/9851693. PMID: 36017130 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Biomaterials for neuroengineering: applications and challenges.Regen Biomater. 2025 Feb 21;12:rbae137. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae137. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40007617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu F, Li L, Lu W, et al. Scutellarin ameliorates cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin and MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:105954. - PubMed
-
- Xu LJ, Chen RC, Ma XY, et al. Scutellarin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytomedicine. 2020;68:153169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
