Proportion of rapid eye movement sleep related obstructive sleep apnea (REM related OSA) in patients with sleep disordered breathing: A cross sectional study
- PMID: 34975051
- PMCID: PMC8926229
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_64_21
Proportion of rapid eye movement sleep related obstructive sleep apnea (REM related OSA) in patients with sleep disordered breathing: A cross sectional study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) during rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep is gaining importance in recent years. This study was done to determine the proportion of REM-related OSA and its associated polysomnographic features.
Methods: One hundred forty-two patients were included in the study. REM-related OSA was defined based on previously established broad and strict criteria (REM apnea-hypopnea index [AHI]/non-REM [NREM] AHI ratio ≥2 and REM AHI >5 with NREM AHI <5, respectively), and its association with polysomnographic features was studied using appropriate statistical tools.
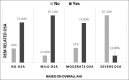
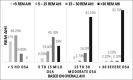
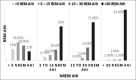
Results: The proportion of REM-related OSA in the study was 56.3% and 25.3% as per broad and strict criterion, respectively. The REM-related OSA group had a mean younger age (47.4 ± 13.2 years) as compared to NREM-related OSA group (52.6 ± 15.8 years). Females (34 out of 45; 75.6%) were more likely to have REM-related OSA as compared to males (46 out of 107; 47.4%). Supine AHI, arousal index, oxygen desaturation index, length of the longest event, and the lowest oxygen saturation recorded during sleep had a significant association with REM-related OSA. 74% of patients with overall AHI <5 and 87% patients with overall AHI 5 to 15 satisfied the criteria for REM-related OSA as per broad criterion.
Conclusion: REM-related OSA was quite prevalent in the study population (56.3%) and was more common in the mild and moderate severity subgroups of OSA.
Keywords: Obstructive sleep apnea; polysomnography; rapid eye movement sleep; sleep apnea syndromes.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obstructive sleep apnea related to rapid-eye-movement or non-rapid-eye-movement sleep: comparison of demographic, anthropometric, and polysomnographic features.J Bras Pneumol. 2016 Jan-Feb;42(1):48-54. doi: 10.1590/S1806-37562016000000012. J Bras Pneumol. 2016. PMID: 26982041 Free PMC article.
-
NREM-AHI greater than REM-AHI versus REM-AHI greater than NREM-AHI in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: clinical and polysomnographic features.Sleep Breath. 2011 Sep;15(3):463-70. doi: 10.1007/s11325-010-0358-z. Epub 2010 May 6. Sleep Breath. 2011. PMID: 20443068
-
Clinical Characteristics of Rapid Eye Movement-Related Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An Experience in a Tertiary Medical Center of Taiwan.Nat Sci Sleep. 2022 Aug 31;14:1521-1532. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S368659. eCollection 2022. Nat Sci Sleep. 2022. PMID: 36068886 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in clinical research of REM-related obstructive sleep apnea].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Feb;36(2):145-148. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.015. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35172555 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Neurocognitive, mood changes, and sleepiness in patients with REM-predominant obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Breath. 2023 Mar;27(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/s11325-022-02602-5. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Sleep Breath. 2023. PMID: 35318576 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Sleep Stage on the Determination of Positional Dependency in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Aug;17(3):226-233. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2023.00037. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38898811 Free PMC article.
-
REM obstructive sleep apnea: prevalence and clinical associations in a high-altitude population.J Clin Sleep Med. 2025 May 1;21(5):835-842. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.11556. J Clin Sleep Med. 2025. PMID: 39797404
-
Differential analysis of clinical outcomes in cerebral infarction associated with REM-OSA and NREM-OSA: a retrospective database study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 15;16:1607963. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1607963. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40734824 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbed Sleep is Not Good for the Heart: A Narrative Review.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023;19(3):e301122211378. doi: 10.2174/1573403X19666221130100141. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36453501 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iber C. Sleep-related breathing disorders. Neurol Clin. 2005;23:1045–57. - PubMed
-
- Guilleminault C, Tilkian A, Dement WC. The sleep apnea syndromes. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:465–84. - PubMed
-
- Guilleminault C. Obstructive sleep apnea. The clinical syndrome and historical perspective. Med Clin North Am. 1985;69:1187–203. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

