Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced penile cancer: an updated evidence
- PMID: 34975068
- PMCID: PMC8887093
- DOI: 10.4103/aja202188
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced penile cancer: an updated evidence
Abstract
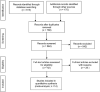
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has shown promising results in patients with locally advanced penile cancer. However, no consensus exists on its applications for locally advanced penile cancer. Thus, it is unclear which kind of chemotherapy regimen is the best choice. Consequently, a systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE was performed in March 2021 to assess the efficacy and safety of NAC for the treatment of patients with locally advanced penile cancer. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was used to assess the risk of bias in each study. This study synthesized 14 published studies. The study revealed that patients who achieved an objective response to NAC obtained a better survival outcome compared with those who did not achieve an objective response. In addition, the objective response rates (ORRs) and pathological complete response (pCR) rates were 0.57 and 0.11, respectively. The incidence of grade ≥3 toxicity was 0.36. Subgroup analysis found that the ORR and pCR of the taxane-platinum (TP) regimen group performed better than those of the nontaxane-platinum (NTP) regimen group (0.57 vs 0.54 and 0.14 vs 0.07, respectively). Moreover, the TP regimen group had more frequent toxicity than the NTP regimen group (0.41 vs 0.26). However, further studies were warranted to confirm the findings.
Keywords: chemotherapy regimen; locally advanced penile cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; response rate.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures




References
-
- Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC. Penile carcinoma: a challenge for the developing world. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:240–7. - PubMed
-
- Pham MN, Deal AM, Ferguson JE, 3rd, Wang Y, Smith AB, et al. Contemporary survival trends in penile cancer: results from the national cancer database. Urol Oncol. 2017;35:674.e1–9. - PubMed
-
- Philippou P, Shabbir M, Malone P, Nigam R, Muneer A, et al. Conservative surgery for squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: resection margins and long-term oncological control. J Urol. 2012;188:803–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

