Advances in Metagenomics and Its Application in Environmental Microorganisms
- PMID: 34975791
- PMCID: PMC8719654
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.766364
Advances in Metagenomics and Its Application in Environmental Microorganisms
Abstract
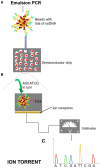
Metagenomics is a new approach to study microorganisms obtained from a specific environment by functional gene screening or sequencing analysis. Metagenomics studies focus on microbial diversity, community constitute, genetic and evolutionary relationships, functional activities, and interactions and relationships with the environment. Sequencing technologies have evolved from shotgun sequencing to high-throughput, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and third-generation sequencing (TGS). NGS and TGS have shown the advantage of rapid detection of pathogenic microorganisms. With the help of new algorithms, we can better perform the taxonomic profiling and gene prediction of microbial species. Functional metagenomics is helpful to screen new bioactive substances and new functional genes from microorganisms and microbial metabolites. In this article, basic steps, classification, and applications of metagenomics are reviewed.
Keywords: antibiotics resistance genes; bioremediation; metagenomics; next-generation sequencing; shotgun sequencing; third generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Chen, Zeng, Xu, Sun, Yang, Bi, Lin, Gao, Hao, Yi, Li and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Apolinar-Hernández M. M., Peña-Ramírez Y. J., Pérez-Rueda E., Canto-Canché B. B., De Los Santos-Briones C., O'Connor-Sánchez A. (2016). Identification and in silico characterization of two novel genes encoding peptidases S8 found by functional screening in a metagenomic library of Yucatán underground water. Gene 593, 154–161. 10.1016/j.gene.2016.08.009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

