Strategies to Circumvent the Side-Effects of Immunotherapy Using Allogeneic CAR-T Cells and Boost Its Efficacy: Results of Recent Clinical Trials
- PMID: 34975869
- PMCID: PMC8714645
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.780145
Strategies to Circumvent the Side-Effects of Immunotherapy Using Allogeneic CAR-T Cells and Boost Its Efficacy: Results of Recent Clinical Trials
Abstract
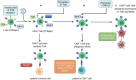
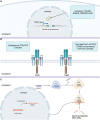
Despite the outstanding results of treatment using autologous chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T cells) in hematological malignancies, this approach is endowed with several constraints. In particular, profound lymphopenia in some patients and the inability to manufacture products with predefined properties or set of cryopreserved batches of cells directed to different antigens in advance. Allogeneic CAR-T cells have the potential to address these issues but they can cause life-threatening graft-versus-host disease or have shorter persistence due to elimination by the host immune system. Novel strategies to create an "off the shelf" allogeneic product that would circumvent these limitations are an extensive area of research. Here we review CAR-T cell products pioneering an allogeneic approach in clinical trials.
Keywords: CAR (chimeric antigen receptor); GvHD; T cell; allogeneic; chimeric; clinical; receptor; trials.
Copyright © 2021 Smirnov, Petukhov, Levchuk, Kulemzin, Staliarova, Lepik, Shuvalov, Zaritskey, Daks and Fedorova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sadelain M, Brentjens R, Rivière I. The Basic Principles of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Design. Cancer Discov (2013) 3(4):388–98. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0548 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

