Enriched Environment Regulates Dendritic Cells to Alleviate Inflammation in Cerebral Infarction Lesions
- PMID: 34976103
- PMCID: PMC8719993
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1574109
Enriched Environment Regulates Dendritic Cells to Alleviate Inflammation in Cerebral Infarction Lesions
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Enriched Environment Regulates Dendritic Cells to Alleviate Inflammation in Cerebral Infarction Lesions.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9805968. doi: 10.1155/2023/9805968. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946987 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to investigate the role that enriched environment (EE) plays in the regulation of inflammation in cerebral infarction (CI) lesions and further explore the relationship between this regulation and dendritic cells (DCs).
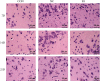
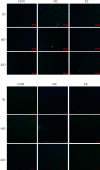
Methods: 72 Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into sham operation group (CON group, n = 24) and CI model group (n = 48). On completion of the establishment of CI rat models by Longa's method, rats in the models group were further assigned to standard environment group (NC group, n = 24) and EE group (n = 24). HE staining was utilized for evaluation of neuronal injury in the lesions. The number of CD74- and integrin αE-positive cells was detected by immunofluorescence. The expression of the IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the brain tissue and serum of rats was measured by immunohistochemistry and ELISA, respectively.
Results: In comparison with the CON group, the NC and EE groups showed significant increases in neuronal injury, CD74- and Integrin αE-positive cells, DC content, as well as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α expression in brain tissue and serum. According to the further comparison between the NC group and EE group, the latter showed decreases in each indicator, and these decreases were in a time-dependent manner.
Conclusion: EE avoids the accumulation of DCs in the lesions and reduces the contents of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, consequently promoting the recovery of CI. And better recovery results can be obtained through increasing the time to stay in EE.
Copyright © 2021 Zhenzhen Zhong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim that there is no conflict of interest between them.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mifepristone alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by stimulating PPAR γ.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Sep;22(17):5688-5696. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201809_15836. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30229846
-
[Effect of scalp-acupuncture on plasma and cerebral TNF-alpha and IL-1beta contents in acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008 Jun;33(3):173-8. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008. PMID: 18807719 Chinese.
-
[Acupuncture ameliorates neurological function by suppressing microglia polarization and inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia in rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Nov 25;47(11):941-48. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210988. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36453669 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Tongdu Tiaoshen electroacupuncture pretreatment on PPARγ-mediated pyroptosis of cerebral cortex in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023 Jul 12;43(7):783-92. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20221010-k0004. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37429658 Chinese.
-
Effects of enriched environment on microglia and functional white matter recovery in rats with post stroke cognitive impairment.Neurochem Int. 2022 Mar;154:105295. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105295. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Neurochem Int. 2022. PMID: 35121010
Cited by
-
Environmental enrichment enhanced neurogenesis and behavioral recovery after stroke in aged rats.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Sep 8;15(18):9453-9463. doi: 10.18632/aging.205010. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37688770 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Enriched Environment Regulates Dendritic Cells to Alleviate Inflammation in Cerebral Infarction Lesions.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9805968. doi: 10.1155/2023/9805968. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37946987 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

