Anticancer properties of colicin E7 against colon cancer
- PMID: 34976246
- PMCID: PMC8690953
- DOI: 10.5114/pg.2021.109622
Anticancer properties of colicin E7 against colon cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer is a major public health problem in the modern world. Every year, new cases of cancer are diagnosed around the world. Cancer cells are altered cells that have escaped the mechanisms that regulate natural growth. Bacteriocins are cationic peptides synthesized by ribosomes that are secreted by almost all groups of bacteria. Some bacteriocins have shown selective toxicity to cancer cells compared to normal cells. This makes them other candidates for research and clinical trials.
Aim: Due to the high prevalence of colon cancer and its therapeutic problems, this study was performed on colicin E7 to evaluate its anti-colon cancer properties.
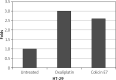
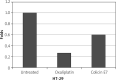
Material and methods: For this reason, colE7 was cloned in pet32c vector and purified protein was affected on HT-29 cells to evaluate the expression of p53 and bcl2.
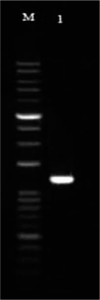
Results: Our in silco analysis demonstrated that colicin E7 has 87.23% confidence as anticancer peptide by ACPred-FL program. First, a PCR reaction was performed using specific primers of the colicin E7 gene, which formed the 1728 bp fragment that belongs to this gene.
Conclusions: Colicin E7 decreased the expression of bcl2 and increased P53. The results of this study showed the general effect of colicin E7 on cancer cells in vitro, which can be evaluated in the future with further experiments.
Keywords: anticancer; colicin E7; colon cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pan ST, Li ZL, He ZX, et al. . Molecular mechanisms for tumour resistance to chemotherapy. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2016; 43: 723-37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
