Ectoine Production from Biogas in Waste Treatment Facilities: A Techno-Economic and Sensitivity Analysis
- PMID: 34976443
- PMCID: PMC8715504
- DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c06772
Ectoine Production from Biogas in Waste Treatment Facilities: A Techno-Economic and Sensitivity Analysis
Abstract
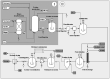
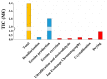
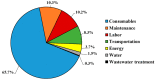
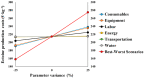
The capacity of haloalkaliphilic methanotrophic bacteria to synthesize ectoine from CH4-biogas represents an opportunity for waste treatment plants to improve their economic revenues and align their processes to the incoming circular economy directives. A techno-economic and sensitivity analysis for the bioconversion of biogas into 10 t ectoine·y-1 was conducted in two stages: (I) bioconversion of CH4 into ectoine in a bubble column bioreactor and (II) ectoine purification via ion exchange chromatography. The techno-economic analysis showed high investment (4.2 M€) and operational costs (1.4 M€·y-1). However, the high margin between the ectoine market value (600-1000 €·kg-1) and the estimated ectoine production costs (214 €·kg-1) resulted in a high profitability for the process, with a net present value evaluated at 20 years (NPV20) of 33.6 M€. The cost sensitivity analysis conducted revealed a great influence of equipment and consumable costs on the ectoine production costs. In contrast to alternative biogas valorization into heat and electricity or into low added-value bioproducts, biogas bioconversion into ectoine exhibited high robustness toward changes in energy, water, transportation, and labor costs. The worst- and best-case scenarios evaluated showed ectoine break-even prices ranging from 158 to 275 €·kg-1, ∼3-6 times lower than the current industrial ectoine market value.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- EBA. Statistical Report of the European Biogas Association 2020. European Biogas Association: Belgium, 2021.
-
- Kaparaju P.; Rintala J.. Generation of heat and power from biogas for stationary applications: boilers, gas engines and turbines, combined heat and power (CHP) plants and fuel cells. In The Biogas Handbook, Science, Production, and Applications; Wellinger A., Murphy J., Baxter D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, 2013; pp 404–427 10.1533/9780857097415.3.404. - DOI
-
- IRENA. Renewable power generation costs in 2018. International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, 2019; pp 11–30.
-
- IRENA. Renewable power generation costs in 2019. International Renewable Energy Agency; Abu Dhabi, 2020, pp 18–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
